Upgrades for familiar agents
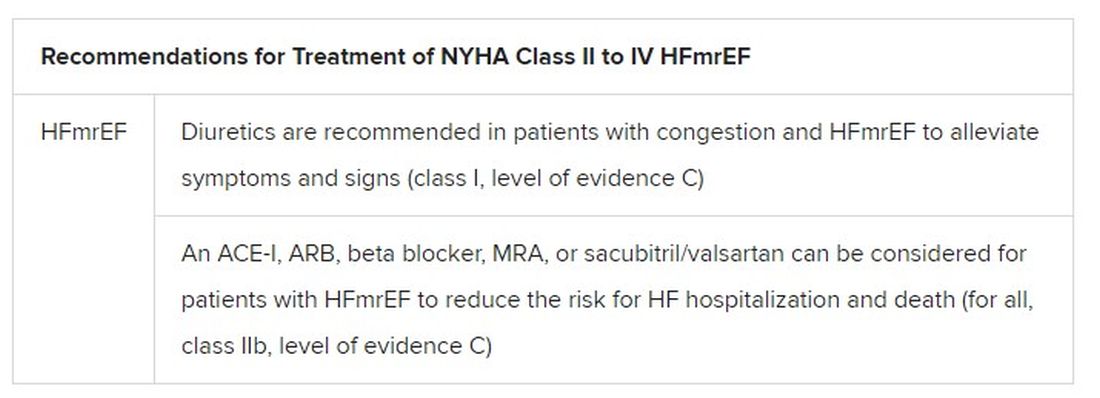
Still, HFmrEF gets noteworthy attention in the document. “For the first time, we have recommendations for these patients,” Dr. Metra said. “We already knew that diuretics are indicated for the treatment of congestion. But now, ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid antagonists, as well as sacubitril/valsartan, may be considered to improve outcomes in these patients.” Their upgrades in the new guidelines were based on review of trials in the CHARM program and of TOPCAT and PARAGON-HF, among others, he said.
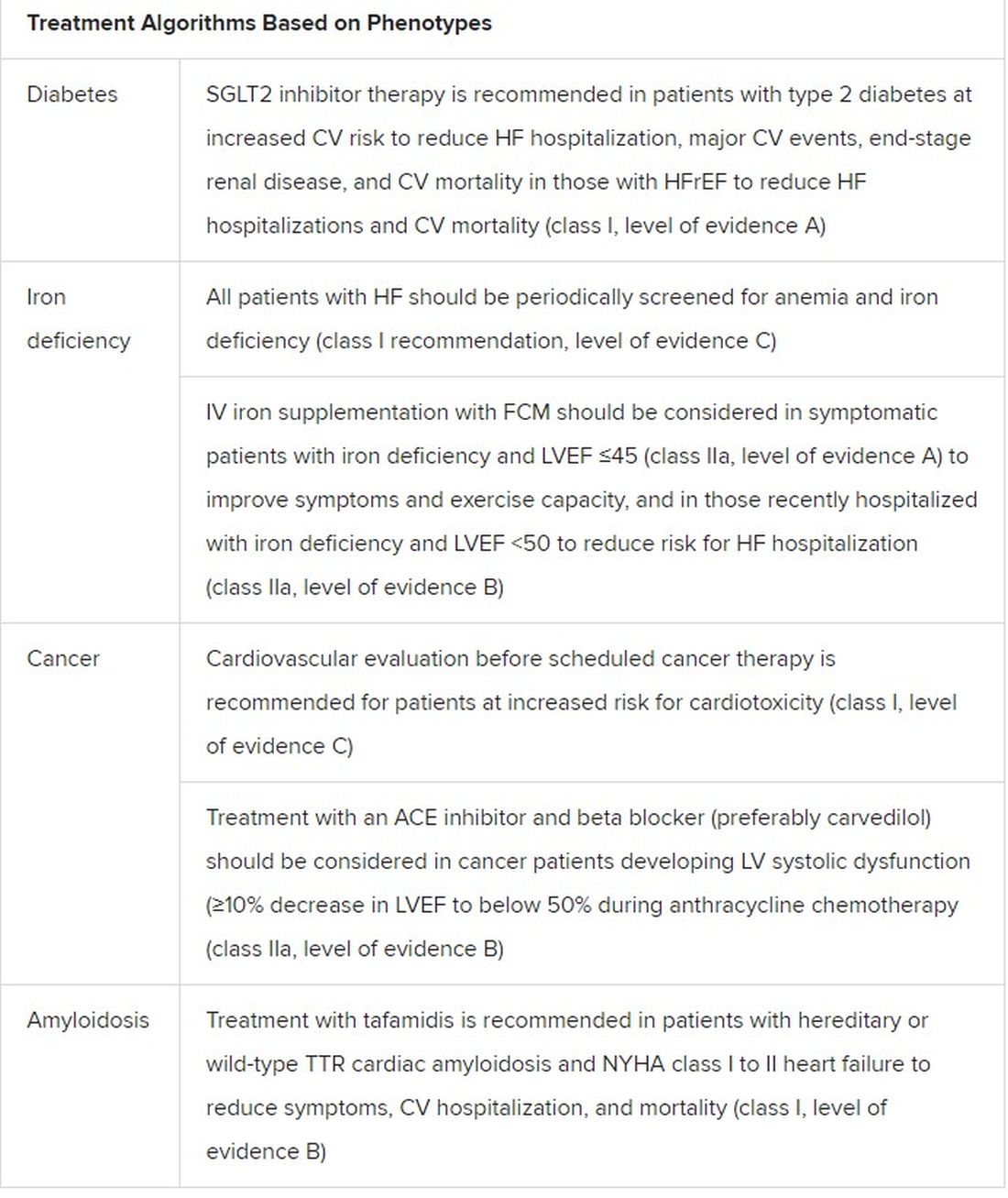
The new document also includes “treatment algorithms based on phenotypes”; that is, comorbidities and less common HF precipitants. For example, “assessment of iron status is now mandated in all patients with heart failure,” Dr. Metra said.
AFFIRM-HF is the key trial in this arena, with its more than 1,100 iron-deficient patients with LVEF less than 50% who had been recently hospitalized for HF. A year of treatment with ferric carboxymaltose (Ferinject/Injectafer, Vifor) led to a 26% drop in risk for HF hospitalization, but without affecting mortality.
For those who are iron deficient, Dr. Metra said, “ferric carboxymaltose intravenously should be considered not only in patients with low ejection fraction and outpatients, but also in patients recently hospitalized for acute heart failure.”
The SGLT2 inhibitors are recommended in HFrEF patients with type 2 diabetes. And treatment with tafamidis (Vyndaqel, Pfizer) in patients with genetic or wild-type transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis gets a class I recommendation based on survival gains seen in the ATTR-ACT trial.
Also recommended is a full CV assessment for patients with cancer who are on cardiotoxic agents or otherwise might be at risk for chemotherapy cardiotoxicity. “Beta-blockers and ACE inhibitors should be considered in those who develop left ventricular systolic dysfunction after anticancer therapy,” Dr. Metra said.
The ongoing pandemic made its mark on the document’s genesis, as it has with most everything else. “For better or worse, we were a ‘COVID guideline,’ ” Dr. McDonagh said. The writing committee consisted of “a large task force of 31 individuals, including two patients,” and there were “only two face-to-face meetings prior to the first wave of COVID hitting Europe.”
The committee voted on each of the recommendations, “and we had to have agreement of more than 75% of the task force to assign a class of recommendation or level of evidence,” she said. “I think we did the best we could in the circumstances. We had the benefit of many discussions over Zoom, and I think at the end of the day we have achieved a consensus.”
With such a large body of participants and the 75% threshold for agreement, “you end up with perhaps a conservative guideline. But that’s not a bad thing for clinical practice, for guidelines to be conservative,” Dr. McDonagh said. “They’re mainly concerned with looking at evidence and safety.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.