Meralgia paresthetica (MP) is a sensory mononeuropathy of the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve (LFCN), clinically characterized by numbness, pain, and paresthesias involving the anterolateral aspect of the thigh. Estimates of MP incidence are derived largely from observational studies and reported to be about 3.2 to 4.3 cases per 10,000 patient-years.1,2 Although typically arising during midlife and especially in the context of comorbid obesity, diabetes mellitus (DM), and excessive alcohol consumption, MP may occur at any age, and bears a slight predilection for males.2-4
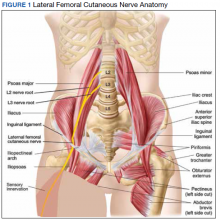
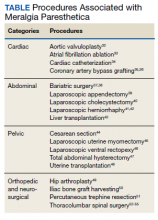
MP may be divided etiologically into iatrogenic and spontaneous subtypes.5 Iatrogenic cases generally are attributable to nerve injury in the setting of direct or indirect trauma (such as with patient malpositioning) arising in the context of multiple forms of procedural or surgical intervention (Table). Spontaneous MP is primarily thought to occur as a result of LFCN compression at the level of the inguinal ligament, wherein internal or external pressures may promote LFCN entrapment and resultant functional disruption (Figure 1).6,7
External forces, such as tight garments, wallets, or even elements of modern body armor, have been reported to provoke MP.8-11 Alternatively, states of increased intraabdominal pressure, such as obesity, ascites, and pregnancy may predispose to LFCN compression.2,12,13 Less commonly, lumbar radiculopathy, pelvic masses, and several forms of retroperitoneal pathology may present with clinical symptomatology indistinguishable from MP.14-17 Importantly, many of these represent must-not-miss diagnoses, and may be suggested via a focused history and physical examination.
Here, we present a case of MP secondary to a massive retroperitoneal sarcoma, ultimately drawing renewed attention to the known association of MP and retroperitoneal pathology, and therein highlighting the utility of a dedicated review of systems to identify red-flag features in patients who present with MP and a thorough abdominal examination in all patients presenting with focal neurologic deficits involving the lower extremities.
Case Presentation
A male Vietnam War veteran aged 69 years presented to a primary care clinic at West Roxbury Veterans Affairs Medical Center (WRVAMC) in Massachusetts with progressive right lower extremity numbness. Three months prior to this visit, he was evaluated in an urgent care clinic at WRVAMC for 6 months of numbness and increasingly painful nocturnal paresthesias involving the same extremity. A targeted physical examination at that visit revealed an obese male wearing tight suspenders, as well as focally diminished sensation to light touch involving the anterolateral aspect of the thigh, extending from just below the right hip to above the knee. Sensation in the medial thigh was spared. Strength and reflexes were normal in the bilateral lower extremities. An abdominal examination was not performed. He received a diagnosis of MP and counseled regarding weight loss, glycemic control, garment optimization, and conservative analgesia with as-needed nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. He was instructed to follow-up closely with his primary care physician for further monitoring.
During the current visit, the patient reported 2 atraumatic falls the prior 2 months, attributed to escalating right leg weakness. The patient reported that ascending stairs had become difficult, and he was unable to cross his right leg over his left while in a seated position. The territory of numbness expanded to his front and inner thigh. Although previously he was able to hike 4 miles, he now was unable to walk more than half of a mile without developing shortness of breath. He reported frequent urination without hematuria and a recent weight gain of 8 pounds despite early satiety.
His medical history included hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, truncal obesity, noninsulin dependent DM, coronary artery disease, atrial flutter, transient ischemic attack, and benign positional paroxysmal vertigo. He was exposed to Agent Orange during his service in Vietnam. Family history was notable for breast cancer (mother), lung cancer (father), and an unspecified form of lymphoma (brother). He had smoked approximately 2 packs of cigarettes daily for 15 years but quit 38 years prior. He reported consuming on average 3 alcohol-containing drinks per week and no illicit drug use. He was adherent with all medications, including furosemide 40 mg daily, losartan 25 mg daily, metoprolol succinate 50 mg daily, atorvastatin 80 mg daily, metformin 500 mg twice daily, and rivaroxaban 20 mg daily with dinner.
His vital signs included a blood pressure of 123/58 mmHg, a pulse of 74 beats per minute, a respiratory rate of 16 breaths per minute, and an oxygen saturation of 94% on ambient air. His temperature was recorded at 96.7°F, and his weight was 234 pounds with a body mass index (BMI) of 34. He was well groomed and in no acute distress. His cardiopulmonary examination was normal. Carotid, radial, and bilateral dorsalis pedis pulsations were 2+ bilaterally, and no jugular venous distension was observed at 30°. The abdomen was protuberant. Nonshifting dullness to percussion and firmness to palpation was observed throughout right upper and lower quadrants, with hyperactive bowel sounds primarily localized to the left upper and lower quadrants.
Neurologic examination revealed symmetric facies with normal phonation and diction. He was spontaneously moving all extremities, and his gait was normal. Sensation to light touch was severely diminished throughout the anterolateral and medial thigh, extending to the level of the knee, and otherwise reduced in a stocking-type pattern over the bilateral feet and toes. His right hip flexion, adduction, as well as internal and external rotation were focally diminished to 4- out of 5. Right knee extension was 4+ out of 5. Strength was otherwise 5 out of 5. The patient exhibited asymmetric Patellar reflexes—absent on the right and 2+ on the left. Achilles reflexes were absent bilaterally. Straight-leg raise test was negative bilaterally and did not clearly exacerbate his right leg numbness or paresthesias. There were no notable fasciculations. There was 2+ bilateral lower extremity pitting edema appreciated to the level of the midshin (right greater than left), without palpable cords or new skin lesions.
Upon referral to the neurology service, the patient underwent electromyography, which revealed complex repetitive discharges in the right tibialis anterior and pattern of reduced recruitment upon activation of the right vastus medialis, collectively suggestive of an L3-4 plexopathy. The patient was admitted for expedited workup.
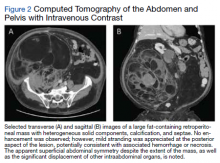
A complete blood count and metabolic panel that were taken in the emergency department were normal, save for a serum bicarbonate of 30 mEq/L. His hemoglobin A1c was 6.6%. Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis with IV contrast was obtained, and notable for a 30 cm fat-containing right-sided retroperitoneal mass with associated solid nodular components and calcification (Figure 2). No enhancement of the lesion was observed. There was significant associated mass effect, with superior displacement of the liver and right hemidiaphragm, as well as superomedial deflection of the right kidney, inferior vena cava, and other intraabdominal organs. Subsequent imaging with a CT of the chest, as well as magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, were without evidence of metastatic disease.
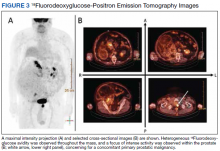
18Fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) was performed and demonstrated heterogeneous FDG avidity throughout the mass (SUVmax 5.9), as well as poor delineation of the boundary of the right psoas major, consistent with muscular invasion (Figure 3). The FDG-PET also revealed intense tracer uptake within the left prostate (SUVmax 26), concerning for a concomitant prostate malignancy.
To facilitate tissue diagnosis, the patient underwent a CT-guided biopsy of the retroperitoneal mass. Subsequent histopathologic analysis revealed a primarily well-differentiated spindle cell lesion with occasional adipocytic atypia, and a superimposed hypercellular element characterized by the presence of pleomorphic high-grade spindled cells. The neoplastic spindle cells were MDM2-positive by both immunohistochemistry and fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH), and negative for pancytokeratin, smooth muscle myosin, and S100. The findings were collectively consistent with a dedifferentiated liposarcoma (DDLPS).
Given the focus of FDG avidity observed on the PET, the patient underwent a transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy of the prostate, which yielded diagnosis of a concomitant high-risk (Gleason 4+4) prostate adenocarcinoma. A bone scan did not reveal evidence of osseous metastatic disease.