Conclusion
- Overall, the study found a statistically significant but modest increased likelihood of remission during 12 weeks of augmentation treatment with aripiprazole, compared with switching to bupropion monotherapy.
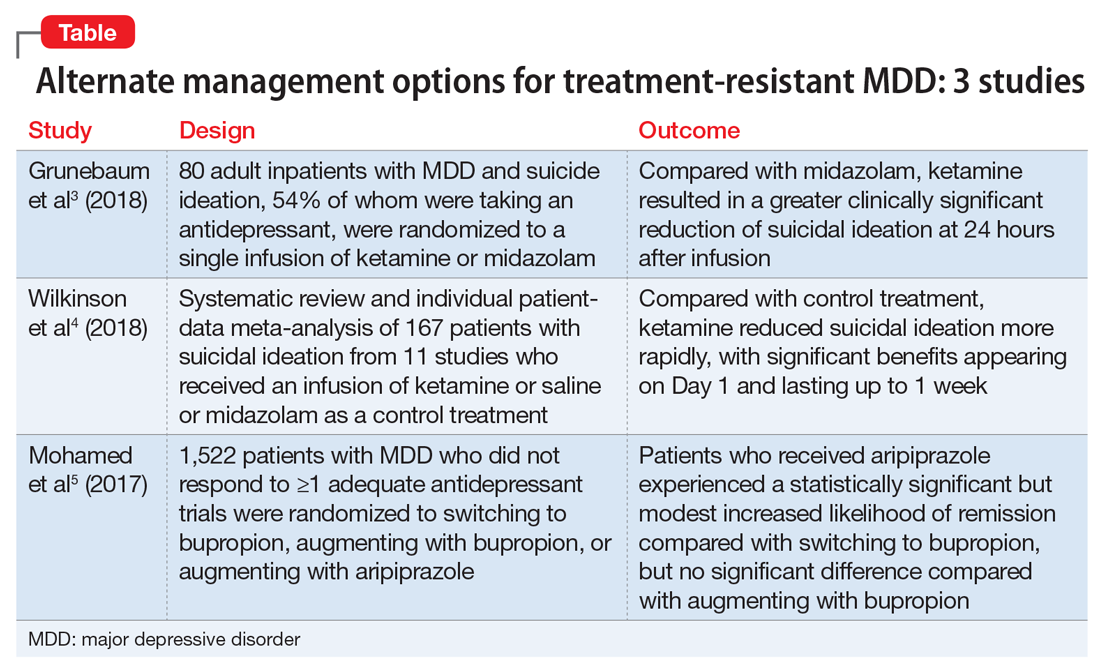
The studies discussed here, which are summarized in the Table,3-5 provide some potential avenues for research into interventions for patients who are acutely suicidal and those with treatment-resistant depression. Further research into long-term outcomes and adverse effects of ketamine use for suicidality in patients with depression is needed. The VAST-D trial suggests a need for further exploration into the efficacy of augmentation with second-generation antipsychotics for treatment-resistant depression.