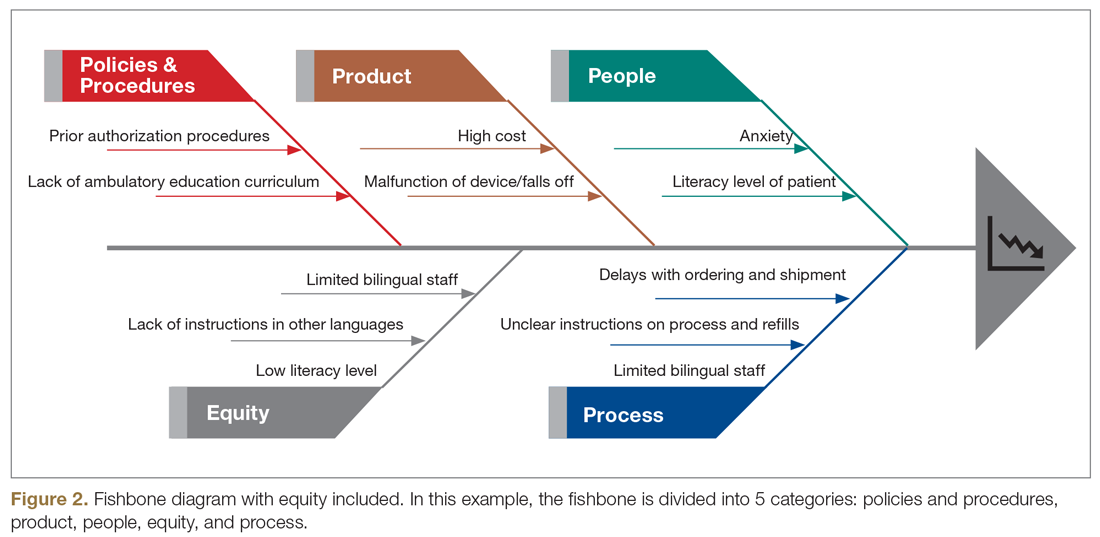
Step 5: Identify how socioeconomic factors are contributing to the current outcome. A good understanding of factors that contribute to the problem is an essential part of finding fundamental solutions. The fishbone diagram16 is a visualization tool used to identify contributing factors. When investigating contributing factors, it is commonplace to identify factors that fit into 1 of 5 categories: people, process, place, product, and policies (5 Ps). An equity-focused process will include equity as a new major factor category, and the socioeconomic impacts that contribute to inequities will be brainstormed and visually represented. For example, in the hypothetical CGM improvement example, an equity contributing factor is extensive CGM application paperwork for patients on public insurance as compared to those on private insurance. Figure 2 shows equity integrated into a fishbone diagram.
Step 6: Brainstorm possible improvements. Potential improvement ideas for the hypothetical CGM example might include redesigning the existing workflow, piloting CGM educational classes, and using a CGM barrier assessment tool to identify and address barriers to adoption.
Step 7: Use the decision matrix with equity as a criterion to prioritize improvement ideas. Decision matrix15 is a great tool that is frequently used to help teams prioritize potential ideas. Project team members must decide what criteria are important in prioritizing ideas to implement. Common criteria include implementation cost, time, and resources, but in addition to the common criteria, the team can specify ”impact on equity” as one of their criteria, alongside other standard criteria like impact.
Step 8: Test one small change at a time. This step is consistent with other traditional improvement models using the Plan, Do, Study, Act (PDSA) model for improvement.17 During this phase, the team should make predictions on the expected impact of the intervention on outcomes. For example, in the hypothetical example, the team predicts that testing and expanding CGM classes will reduce disparities among public versus private health insurance users by 5% and increase overall CGM uptake by 10%.
Step 9: Measure and compare results with predictions to identify inequitable practices or consequences. After each test of change, the team should review the results, including implementation cost considerations, and compare them to the predictions in the earlier step. The team should also document the potential reasons why their predictions were correct or inaccurate, and whether there were any unforeseen outcomes from the intervention.
Step 10: Celebrate small wins and repeat the process. Making fundamental and equitable changes takes time. This framework aimed at undoing inequities, particularly those inequities that have been amplified by the COVID-19 pandemic, is iterative and ongoing.18,19 Not every test of change will impact the outcome or reduce inequity, but over time, each change will impact the next, generating sustainable effects.