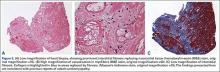
Additional workup was initiated, and cardiac catheterization showed that the patient continued to decompensate, with worsening global left ventricular dysfunction with an ejection fraction of 30% without evidence of coronary artery disease. Also, he was noted to have mild renal impairment with a blood urea nitrogen level of 31 mg/dL and a creatinine level of 1.7 mg/dL. The etiology of the renal impairment was unknown and had not been established, according to the patient and his wife. The renal impairment was not thought to be caused by the elevated metal ions levels but likely resulted from prerenal azotemia secondary to decreased cardiac output. During catheterization, an endomyocardial biopsy was performed and the tissue sent to the Mayo Clinic pathology department for analysis. The sample showed myocyte hypertrophy and interstitial fibrosis with scattered myofibers containing large cytoplasmic vacuoles. Also present was karyomegaly consistent with myocyte hypertrophy (Figures 2A, 2B). Trichrome stain confirmed replacement of myofibers by collagen (Figure 2C). Electron microscopy performed on a paraffin block showed reduced contractile elements, vacuolar spaces, and increased lipofuscin. The findings were very consistent with, but not specific for, cardiomyopathy from cobalt toxicity. No evidence of an inflammatory infiltrate was identified. The diagnosis was cobalt cardiomyopathy based on biopsy, presentation, cobalt levels, and intraoperative findings.
The patient was admitted to the cardiac intensive care unit preoperatively and optimized with inotropic agents. A multidisciplinary consultation with the cardiology and anesthesia departments was obtained. Both recommended cardiac anesthesia with intraoperative Swan-Ganz catheter and transesophageal echo monitoring. Assuming that the patient remained hemodynamically stable with limited blood loss and the first hip was timely performed, the cardiology department recommended a single surgery, because fewer risks and complications could be expected than from a staged procedure. Subsequently, surgery was performed on the left hip via a conservative anterior approach on the fracture table. The patient remained stable with limited blood loss. During the same operating room time, revision of the right hip was performed using an anterior approach. The intraoperative findings showed evidence of pseudotumors in the adjacent soft tissues and abundant brown, creamy fluid upon entering the joint capsule, consistent with a metallic appearance. Both hips showed similar prosthetic findings. There was no significant visible wear of the large diameter metal heads or gross abnormality of the acetabular components. The trunnion area on both femoral implants was abnormal, revealing a black coating suggestive of marked corrosion. The components were all well fixed, without visible damage, and, because of his fragile cardiac status, the patient’s acetabular components were not revised. The trunnions were cleaned and the femoral heads were revised to active articulation dual-mobility metal-on-polyethylene constructs using 28-mm Biolox Option ceramic (CeramTec). The tissue specimens from the operation showed chronic inflammation with areas of fibroconnective tissue and bland fibrinoid necrosis with extensive brown pigment-laden macrophage reaction. The intraoperative cultures were negative.
The patient tolerated the surgery without complication, and his postoperative period was without incident. Nine months after surgery, the patient’s cobalt and chromium levels had declined to 16 ppb and 32 ppb, respectively (normal, <1 ppb). However, his cardiac status continued to worsen with significant shortness of breath and bilateral lower extremity edema despite diuresis. Follow-up cardiac MRI indicated progressive left and right dysfunction with ejection fractions of 23% and 25%, respectively. After progressive heart-failure symptoms, the patient was admitted to the hospital for severe congestive heart failure and underwent implantation of a HeartWare LVAD with tricuspid valve repair using an Edwards annuloplasty ring. He has since had a cardiac transplant and is doing well.
Discussion
To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of cardiomyopathy in a patient with elevated cobalt ion levels and a Biomet M2a-Magnum hip prosthesis. This is also the first reported case of cardiac MRI–defined cobalt cardiomyopathy. The cobalt levels seen in this patient were similar to those of other cases with systemic cobalt toxicity from a MOM hip construct. Mao and colleagues5 reported 2 cases of systemic cobalt toxicity in 2 patients with articular surface replacement hip prostheses.One patient presented with mild groin pain, neurologic symptoms, and a cobalt level of 410 ppb 5 years after her index procedure. The other patient presented with cardiac and neurologic symptoms but no hip complaints. The patient’s cobalt levels ranged from 185 ppb to 210 ppb. Both patients improved after their revision surgery, and their cobalt levels decreased. The 2 patients in Tower’s report6 were 49-year-old men who had articular surface replacement implants (DePuy). One patient who presented with progressive hip pain 11 months postoperatively developed neurologic symptoms and cardiomyopathy, with cobalt levels of 83 ppb before revision surgery 43 months after his index procedure. The other patient presented with hip pain and vertigo, headaches, fatigue, and dyspnea. He underwent hip revision 40 months postoperatively and required closed reduction under sedation for dislocation. Finally, and most recently, Allen and colleagues2 reported a 59-year-old woman with a cobalt level of 287 ppb whose symptoms did not resolve after implantation of an LVAD or cardiac transplantation but only after removal of her bilateral hip prosthesis. Our case is most similar to this report but significantly adds to the literature in 2 distinct manners: (1) Biomet M2a-Magnum has not been implicated in cobalt toxicity; and (2) this is the first reported use of dedicated cardiac MRI to noninvasively define underlying cardiac pathology.