TECHNIQUE: ILIAC CREST (PSIS) BONE MARROW ASPIRATION
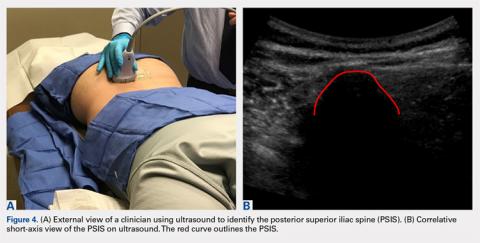
The patient is brought to the procedure room and placed in a prone position. The donor site is prepared and draped in the usual sterile manner. Ultrasound is used to identify the median sacral crest in a short-axis view. The probe is then moved laterally to identify the PSIS (Figures 4A, 4B).
The probe can be moved superiorly and inferiorly to determine the most prominent and central portion of the PSIS. The SI joint and ilium can also be visualized if needed.The crosshairs on the ultrasound probe are used to mark the center lines of each plane. The central point marks the location of the PSIS. Alternatively, an in-plane technique can be used to place a spinal needle on the exact entry point on the PSIS. Once the PSIS and entry point are identified, the site is blocked with 10 mL of 0.5% ropivacaine.
Prior to introduction of the trocar, all instrumentation is primed with heparin and syringes are prepped with anticoagulant citrate dextrose solution, solution A. A stab incision is made at the site. The trocar is placed at the entry point, which should be centered in a superior-inferior plane and at the most medial point of the PSIS. Starting with the trocar vertical, the trocar is angled laterally 24° by dropping the hand medially toward the midline. No angulation cephalad or caudad is necessary, but cephalad must be avoided so as not to skive superiorly. This angle, which is recommended for both males and females, allows for the greatest distance the trocar can travel in bone before hitting the anterior ilium wall. A standard deviation of 5.57° is present, which should be considered. Steady pressure should be applied with a slight twisting motion on the PSIS. If advancement of the trocar is too difficult, a mallet or drill can be used to assist in penetration.
With the trocar advanced into the bone 1 cm, the trocar needle is removed while the cannula remains in place. The syringe is attached to the top of the cannula. The syringe plunger is pulled back to aspirate 20 mL of bone marrow. The cannula and syringe assembly are advanced 2 cm farther into the bone to allow for aspiration of a new location within the bone marrow cavity, and 20 mL of bone marrow are again aspirated. This is done a final time, advancing the trocar another 2 cm and aspirating a final 20 mL of bone marrow. The entire process should yield roughly 60 mL of bone marrow from one side. If desired, the same process can be repeated for the contralateral PSIS to yield a total of 120 mL of bone marrow from the 2 sites.
Based on our data, the average distance to the anterior ilium wall was 7 cm, but the shortest distance noted in this study was 5 cm. On the basis of the data presented, this technique allows for safe advancement based on even the shortest measured distance, without fear of puncturing the anterior ilium wall. Perforation could damage the femoral nerve and the internal or external iliac artery or vein that lie anterior to the ilium.
Continue to: We hypothesized that there...