Early administration of evolocumab significantly reduced levels of LDL cholesterol in patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention, according to data from an open-label randomized trial of 102 adults in Japan.
Data from previous studies have shown that proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitors can reduce LDL cholesterol in acute coronary syndrome patients, wrote Tomoaki Okada, MD, of Kagawa (Japan) Prefectural Central Hospital and colleagues.
In particular, “The EVOPACS trial [J Am Coll Cardiol 2019; 74:2452-62] reported that evolocumab therapy initiated at an early phase of ACS showed [LDL cholesterol] level reduction by 4-8 weeks,” they said.
“However, the 4-week efficacy of PCSK9 inhibitor therapy combined with a statin remains unknown,” they said.
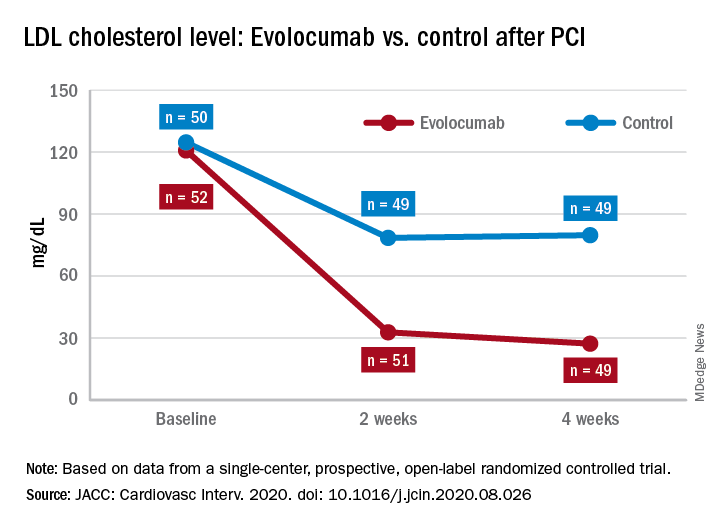
In a study presented at the virtual annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology and published simultaneously in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, the researchers randomized 52 patients to receive 140 mg of evolocumab subcutaneously within 24 hours of indexed percutaneous coronary intervention and again after 2 weeks. A group of 50 controls received evolocumab after PCI only, but no additional dose after 2 weeks.
The average age of the patients was 65 years, 88% were men, and 26% had a history of statin treatment.
A total of 49 patients in each group were included in the final analysis, with a primary outcome of change in LDL cholesterol levels from baseline to 4 weeks.
Baseline LCL cholesterol levels were 120.8 mg/dL and 124.7 mg/dL in the evolocumab and control groups, respectively. Changes from baseline were significantly greater in the evolocumab group, compared with controls, at –76% and –33%, respectively.
All patients in the evolocumab group and 27% of patients in the control groups achieved LDL cholesterol levels of less than 70 mg/dL at 4 weeks. In addition, 92% and 96% of evolocumab patients achieved LDL cholesterol levels less than 55 mg/dL at 2 weeks and 4 weeks, respectively.
Overall changes in non-HDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, and small dense LDL in the evolocumab and control groups were –66.2% and –26.0%; 2.8% and –0.7%; and –67% and –13.8%, respectively. Of these, changes in non-HDL cholesterol and small dense LDL were significantly different between the groups.
In addition, patients in the evolocumab group showed a 3% decrease in lipoprotein, compared with an 82% increase in the control group. This finding suggests the additional benefit of including evolocumab for managing residual risk in patients with high lipoprotein(a) levels” after acute MI, the researchers noted.
Adverse events and serious adverse events were similar between the groups.
‘Early and strong’ LDL cholesterol lowering best for preventing repeat events
“By using the PCSK9 inhibitors, we have the opportunity to lower LDL cholesterol [LDL-C]” both quickly and dramatically, said Heinz Drexel, MD, in an interview.
“This Japanese study shows that very low LDL-C levels can be obtained as fast as within 4 weeks,” he said. “This fits into the concept that risk for future infarctions and strokes is best reduced by early and strong LDL-C lowering,” he explained.
Dr. Drexel said that he was not surprised by the magnitude of the decrease in LDL cholesterol in study findings in light of the EVOPACS study and other research, as well as his own clinical experience.
“The primary message for doctors is that it is now possible to achieve these low levels of LDL-C in a short time,” he said.
“Additional research must prove that this low LDL-C translates to reduction of MIs and strokes, and there is increasing evidence that this will happen,” Dr. Drexel noted.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Drexel had no financial conflicts to disclose.
SOURCE: Okada T et al. ESC 2020. JACC Cardiovascular Interventions. 2020 Aug 28. doi: 10.1016/j.jcin.2020.08.026.