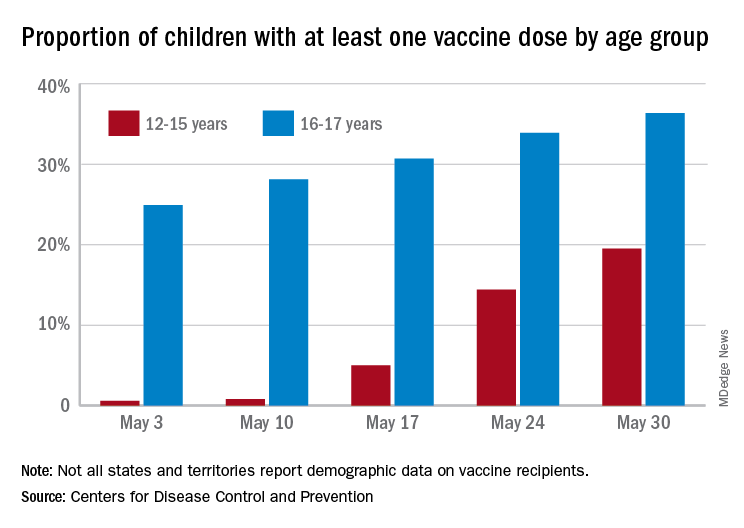
More children aged 12-15 years already have received at least one dose of a COVID-19 vaccine than have 16- and 17-year-olds, based on data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
with those figures representing increases of 31.6% and 6.6% in the past week, respectively. Since the overall size of the 12-15 population is much larger, however, the proportion vaccinated is still smaller: 19.5% to 36.4%, according to the CDC’s COVID Data Tracker.
A look at full vaccination status shows that only 0.7% of those aged 12-15 years have received both doses of a two-dose vaccine or one dose of the single-shot variety, compared with 24% of those aged 16-17. For the country as a whole, 50.5% of all ages have received at least one dose and 40.7% are fully vaccinated, the CDC said.
Children aged 12-15 represent the largest share of the U.S. population (23.4%) initiating vaccination in the 14 days ending May 30, while children aged 16-17 made up just 4.5% of those getting their first dose. The younger group’s later entry into the vaccination pool shows up again when looking at completion rates, though, representing just 0.4% of all Americans who reached full vaccination during that same 14-day period, compared with 4.6% of the older children, the CDC data show.
Not all states are reporting data such as age for vaccine recipients, the CDC noted, and there are other variables that affect data collection. “Demographic data ... might differ by populations prioritized within each state or jurisdiction’s vaccination phase. Every geographic area has a different racial and ethnic composition, and not all are in the same vaccination phase,” the CDC said.