, according to a study in the European Heart Journal.
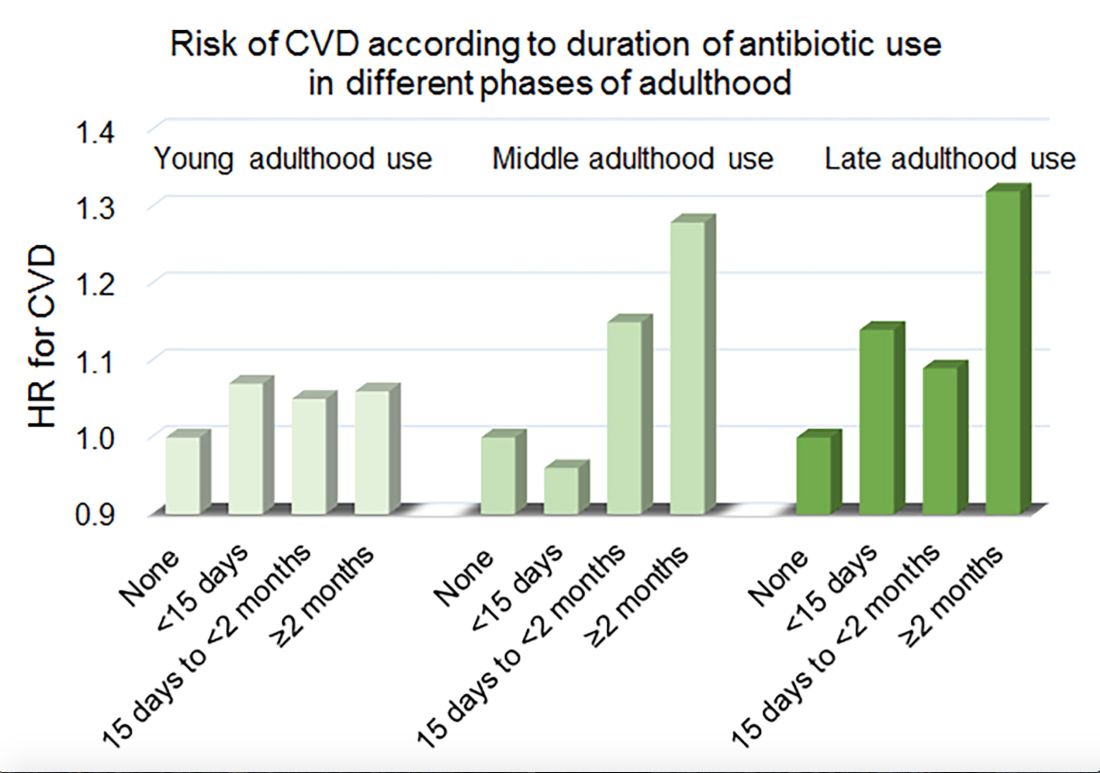
Women in the Nurses’ Health Study who used antibiotics for 2 or more months between ages 40 and 59 years or at age 60 years and older had a significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease, compared with those who did not use antibiotics. Antibiotic use between 20 and 39 years old was not significantly related to cardiovascular disease.
Prior research has found that antibiotics may have long-lasting effects on gut microbiota and relate to cardiovascular disease risk.
“Antibiotic use is the most critical factor in altering the balance of microorganisms in the gut,” said lead investigator Lu Qi, MD, PhD, in a news release. “Previous studies have shown a link between alterations in the microbiotic environment of the gut and inflammation and narrowing of the blood vessels, stroke, and heart disease,” said Dr. Qi, who is the director of the Tulane University Obesity Research Center in New Orleans and an adjunct professor of nutrition at Harvard T.C. Chan School of Public Health in Boston.
To evaluate associations between life stage, antibiotic exposure, and subsequent cardiovascular disease, researchers analyzed data from 36,429 participants in the Nurses’ Health Study. The women were at least 60 years old and had no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer when they completed a 2004 questionnaire about antibiotic usage during young, middle, and late adulthood. The questionnaire asked participants to indicate the total time using antibiotics with eight categories ranging from none to 5 or more years.
The researchers defined incident cardiovascular disease as a composite endpoint of coronary heart disease (nonfatal myocardial infarction or fatal coronary heart disease) and stroke (nonfatal or fatal). They calculated person-years of follow-up from the questionnaire return date until date of cardiovascular disease diagnosis, death, or end of follow-up in 2012.
Women with longer duration of antibiotic use were more likely to use other medications and have unfavorable cardiovascular risk profiles, including family history of myocardial infarction and higher body mass index. Antibiotics most often were used to treat respiratory infections. During an average follow-up of 7.6 years, 1,056 participants developed cardiovascular disease.
In a multivariable model that adjusted for demographics, diet, lifestyle, reason for antibiotic use, medications, overweight status, and other factors, long-term antibiotic use – 2 months or more – in late adulthood was associated with significantly increased risk of cardiovascular disease (hazard ratio, 1.32), as was long-term antibiotic use in middle adulthood (HR, 1.28).
Although antibiotic use was self-reported, which could lead to misclassification, the participants were health professionals, which may mitigate this limitation, the authors noted. Whether these findings apply to men and other populations requires further study, they said.