Problem/Issue
As mentioned above, the older adult population is increasing, and these statistics are reflected in our service area [4]. Exacerbating these demographic changes is a shortage of health care workers in all disciplines, inadequate geriatric training, and the increased prevalence of multiple chronic conditions. Older adults also have higher rates of 30-day readmissions as well as higher rates of functional decline and medical errors during hospital stays [5,6]. Effective interprofessional teamwork is essential for the delivery of high-quality patient care in an increasingly complex health environment [7]. The IOM’s Future of Nursing report recommends that nurses, who represent the largest segment of the US health workforce, should achieve higher levels of training and be full partners in redesigning health care [8]. Unfortunately, effective care is hampered by poor coordination, limited communication, boundary infringement, and lack of understanding of roles [9]. Meta-analyses have demonstrated that there is a positive relationship between team training interventions and outcomes [10,11].
Objectives
The objective of the IGDCC is to elevate the level of geriatric care in the region by providing an accessible and affordable forum for the education of health care workers involved in the care of our most vulnerable population. To meet this challenge, the 4 founding members of IGDCC utilized the Aurora Health Care Geriatric Fellow’s Most Difficult Case (GFMCC) conference format as a model [12,13]. All disciplines are encouraged to participate, with announcements sent out via the leadership at the participating hospital systems. Participants have the option to call into the conference and teleconference via their own personal telephone and computer; in addition, each participating hospital system frequently hosts an open forum teleconference room where participants also may join a group.
Conference Components
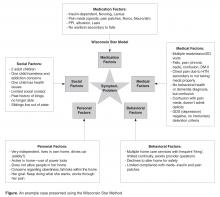
Case calls are typically held the third Thursday of each month over the lunch hour. The case call consists of a 20- to 30-minute case presentation based on a standard template ( Figure), followed by an opportunity for participants to ask questions.The team uses the Wisconsin Star Method framework for presentation and discussion of the case. The Star Method, developed by Timothy Howell, enables clinical data about a person to be mapped out onto a single field with 5 domains: medications, medical, behavioral, personal, and social [14], creating a visual representation of the complicated and interacting physical, emotional, and social issues of older adults (Figure). By becoming comfortable using this method, the learner can use a similar approach in their clinical practice to address the needs of the patient in a holistic manner.
The case call concludes with expert teaching points from both a geriatric expert and a member of the interdisciplinary team. The interdisciplinary team member is chosen based on the key issues raised by the case. For example, cases that are made complex due to polypharmacy and adverse drug reactions might have a pharmacist presenting pertinent take-home message for the learner. In addition, geriatric teaching experts (ie, a geriatrician or advanced practice geriatric nursing specialist) provide the learner with insights that they can apply to their future practice. Often times the teaching points consist of an analysis of the various geriatric syndromes and how they can be managed in the complex older adult.