Andrew N. Wilner, MD, FAAN, FACP
Angels Neurological Centers
Abington, MA
Clinical History
A 37-year-old pregnant African American woman with a history of epilepsy and polysubstance abuse was found unresponsive in a hotel room. She had four convulsions en route to the hospital. In transit, she received levetiracetam and phenytoin, resulting in the cessation of the clinical seizures.
According to her mother, seizures began at age 16 during her first pregnancy, which was complicated by hypertension. She was prescribed medications for hypertension and phenytoin for seizures. The patient provided a different history, claiming that her seizures began 2 years ago. She denied taking medication for seizures or other health problems.
The patient has two children, ages 22 and 11 years. Past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. She has no allergies. Social history includes cigarette smoking, and alcohol and substance abuse. She lives with her boyfriend and does not work. She is 25 weeks pregnant. Family history was notable only for migraine in her mother and grandmother.
Physical Examination
In the emergency department, blood pressure was 135/65, pulse 121 beats per minute, and oxygen saturation was 97%. She was oriented only to self and did not follow commands. Pupils were equal and reactive. There was no facial asymmetry. She moved all 4 extremities spontaneously. Reflexes were brisk. Oral mucosa was dry. She had no edema in the lower extremities.
Laboratories
Chest x-ray was normal. EKG revealed tachycardia and nonspecific ST changes. Hemoglobin was 11.1 g/dl, hematocrit 32%, white blood cell count 10,900, and platelets 181,000. Electrolytes were normal except for a low sodium of 132 mmol/l (135-145) and bicarbonate of 17 mmol/l (21-31). Glucose was initially 67 mg/dl and dropped to 46 mg/dl. Total protein was 6 g/dl (6.7-8.2) and albumin was 2.7 g/dl (3.2-5.5). Metabolic panel was otherwise normal. Urinalysis was positive for glucose, ketones, and a small amount of blood and protein. There were no bacteria. Blood and urine cultures were negative. Phenytoin level was undetectable. Urine drug screen was positive for cannabinoids and cocaine.
Hospital Course
Hypoglycemia was treated with an ampule of D50 and intravenous fluids. On the obstetrics ward, nurses observed several episodes of head and eye deviation to the right accompanied by decreased responsiveness that lasted approximately 30 seconds. The patient was sent to the electrophysiology lab where an EEG revealed a diffusely slow background ( Figure 1 ).
Figure 1. Generalized Slowing
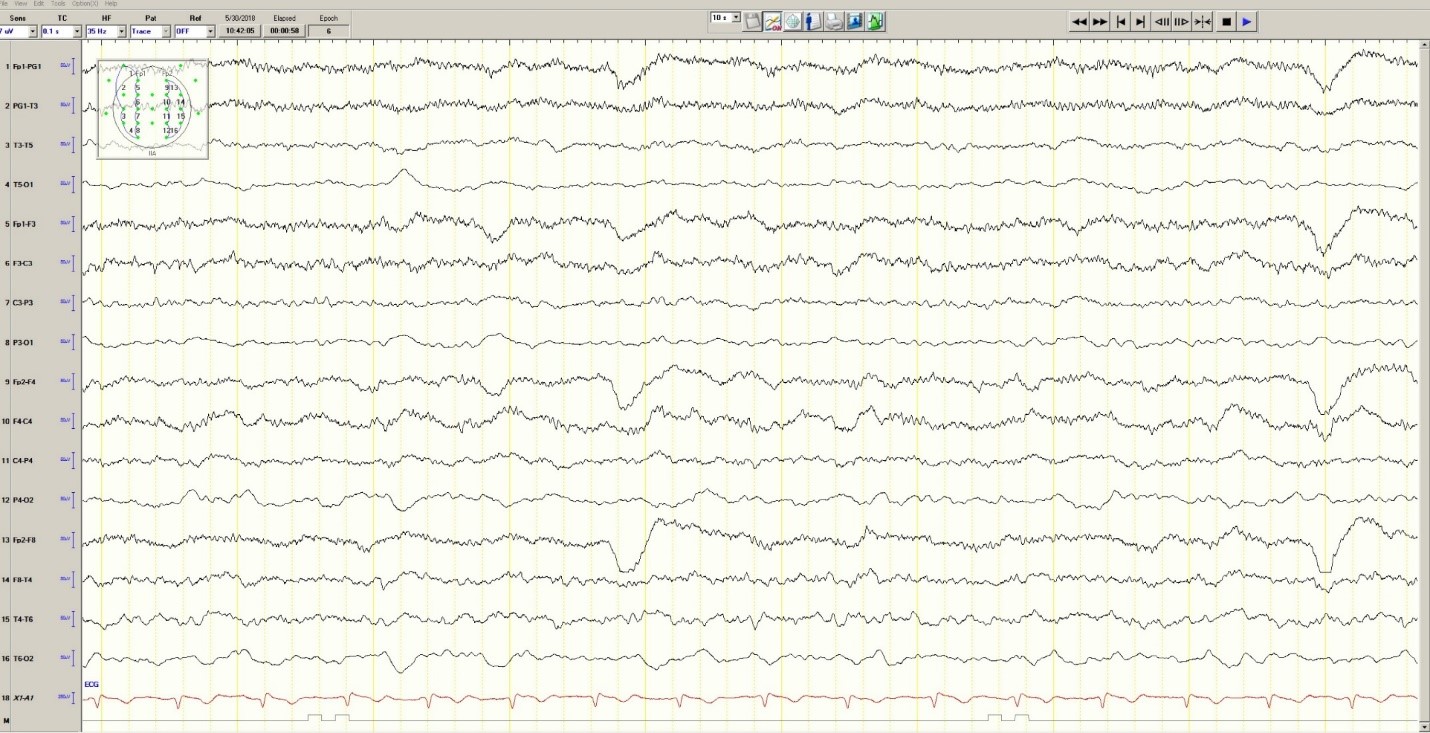
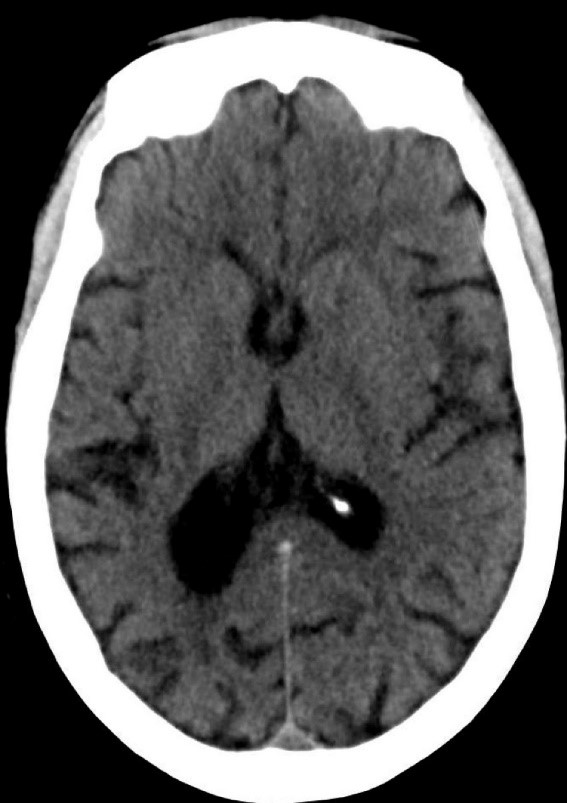
During the 20-minute EEG recording, the patient had six clinical seizures similar to those described by the nurses. These events correlated with an ictal pattern consisting of 11 HZ_sharp activity in the right occipital temporal region that spread to the right parietal and left occipital temporal regions ( Figure 2 ). Head CT revealed mild generalized atrophy and an enlarged right occipital horn, but no acute lesions ( Figure 3 ).
Figure 2. Partial seizure originating in right occipital temporal region
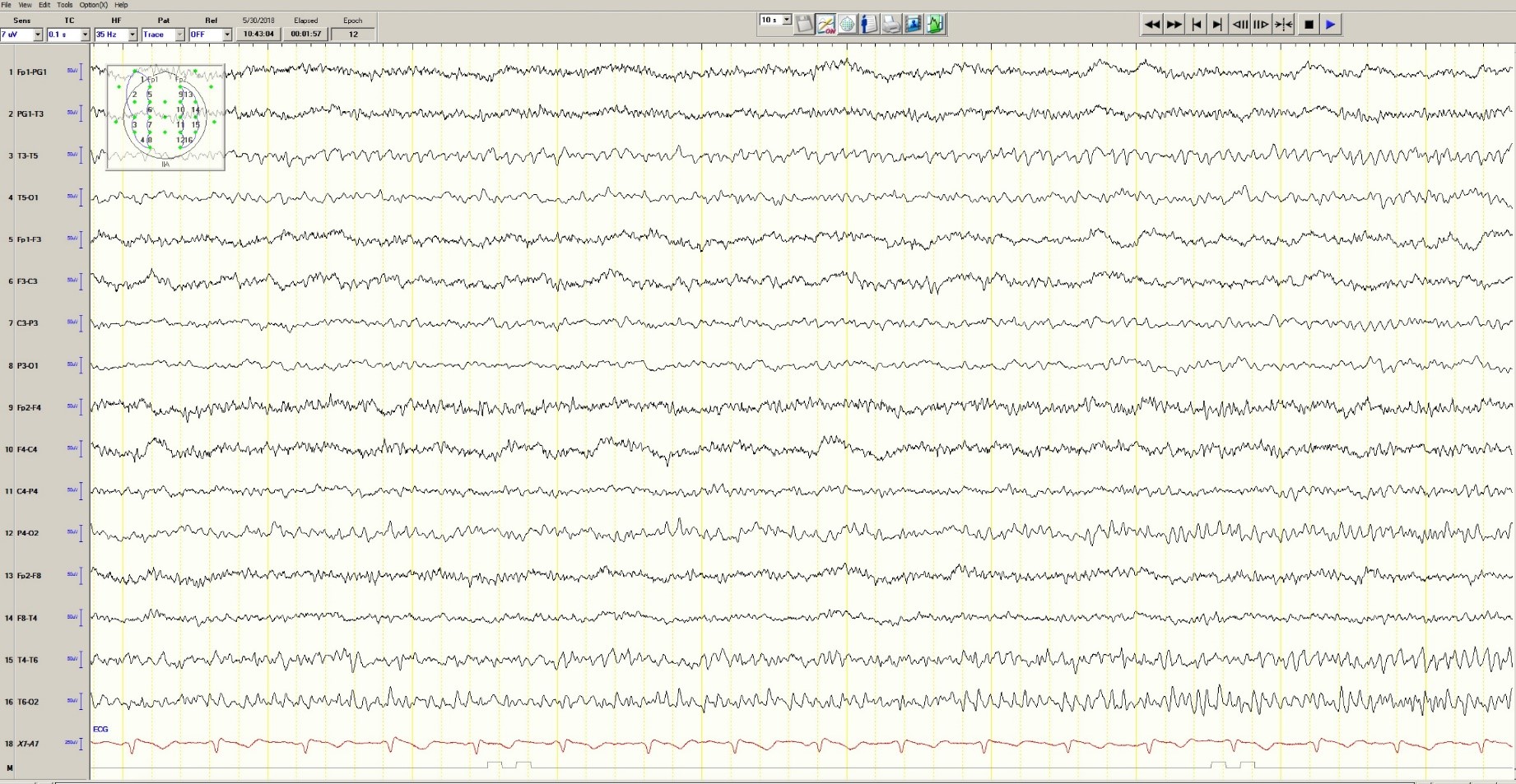
Figure 3. Mild generalized arophy, greater in right hemisphere
The patient was transferred to intensive care and received fosphenytoin. No further clinical and /or electrographic seizures were identified. The following day, an EEG revealed diffuse slowing without focal seizures ( Figure 4 ). The patient gradually became more alert and cooperative over the next 24 hours. However, the next day no fetal heartbeat was detected. Labor was induced and a stillborn baby delivered. The pathology report indicated that the placenta was between the 5 th and 10 th percentile for gestational age.










