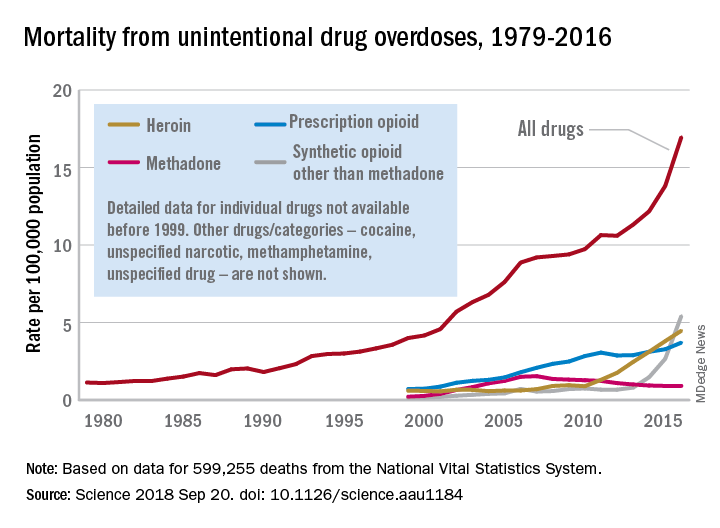
Overdose death rates for individual drugs show no particular patterns since the turn of the century, but the exponential growth of overall drug mortality actually started before the opioid epidemic, according to an analysis of almost 600,000 unintentional overdose deaths since 1979.
“The current epidemic of overdose deaths due to prescription opioids, heroin, and fentanyl appears to be the most recent manifestation of a more fundamental, longer-term process,” senior author Donald S. Burke, MD, of the University of Pittsburgh, said in a written statement.
Overdose mortality from all types of drugs rose from 1.13 per 100,000 population in 1979 to 16.96 per 100,000 in 2016, based on data for 599,255 deaths from unintentional drug overdoses in the National Vital Statistics System, they reported in Science.
When the investigators plotted annual drug overdose mortality over that 38-year period, they saw a smooth upward exponential curve with a doubling time of about 9 years. “This remarkably smooth, long-term epidemic growth pattern really caught our attention,” Dr. Burke said. “If we can figure it out, we should be able to bend that curve downward.”
The individual drug types that make up the whole, however, are a different story. “There is no regular or predictable pattern to the overdose rates for any of these drugs. Cocaine overdose death rates curved down and up and down and back up over the past 20 years. Methadone deaths have been on a downturn since the mid-2000s. Prescription opioids have been on a fairly steady, steep climb. Heroin deaths shot up in 2010, followed in 2013 by synthetic opioids, such as fentanyl,” lead author Hawre Jalal, MD, PhD, also of the university, said in the statement.
Geographic and demographic analyses produced the same absence of patterns. the researchers wrote.
The study was supported by grants from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation. The investigators said they have no competing interests.
SOURCE: Jalal H et al. Science 2018 Sep 20. doi: 10.1126/science.aau1184.