Prostatic leiomyosarcoma is a rare tumor.1 This neoplasm is composed of highly aggressive prostatic smooth muscle cells that present with nonspecific signs and symptoms mimicking other forms of prostatic pathology. Of the primary prostatic sarcomas, leiomyosarcoma represents the most common subtype in adults and is found in 38% to 52% of newly diagnosed prostate sarcoma.1,2 The prognosis is poor, and no clear guidelines exist regarding the optimal treatment approach. We report a case of prostate leiomyosarcoma and describe the disease characteristics, diagnostic modalities, and treatment approach regarding these rare malignancies.
Case Presentation
A 72-year-old male presented with 6 months of progressive severe lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS) secondary to bladder outlet obstruction. The patient was refractory to medical management with combination α-blocker and 5-α-reductase inhibitor therapy and continued to require multiple emergent bladder catheterizations. Workup with urinalysis, blood biochemistry, and prostate specific antigen (PSA) levels were persistently normal. He reported no hematuria, weight loss, or perineal pain. The patient reported no history of tobacco use, exposure to hazardous chemicals, and had no family history of genitourinary cancers. On rectal exam, the prostate was firm and nodular, with induration noted along the right upper lobe of the prostate.
The patient was referred for a urology consultation and subsequently underwent transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP) for suspected severe benign prostatic hypertrophy (BPH). A histopathologic examination demonstrated atypical cytology consistent with high- grade leiomyosarcoma. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed positive staining for vimentin, smooth muscle actin, desmin (partial), cytokeratin, smooth muscle myosin, muscle specific actin, and Ki-67 (50%-60% expression).
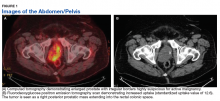
Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) scan revealed a 5.7 x 5.9 cm tumor with a maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax) of 12.6 in the right posterior prostate, without evidence of metastatic disease (Figures 1A and 1B).
The patient was referred to medical and radiation oncology. He was evaluated for radical prostatectomy and planned for surgery with neo-adjuvant radiation. He received palliation of his symptoms with bilateral nephrostomy tubes; however, the patient had significant comorbidities and died prior to treatment.Discussion
Originating from prostatic interstitial cells, prostatic leiomyosarcoma is a rare tumor that accounts for < 0.1% of all primary prostatic malignancies.1 Since its first description in 1950 by Riba and colleagues, < 200 cases have been reported worldwide.2 Among the sarcomas of the prostate, it is the most common tumor, accounting for around 38% to 52% of prostate sarcoma presentations.1,2
Patients typically present between the ages of 41 and 78 years (mean age 61 years).2,3 Signs and symptoms at presentation may vary; however, the most common symptoms are related to lower urinary tract obstruction (89.4% of patients). These symptoms include urinary frequency, urgency, nocturia, and may mimic the presentation of BPH.
Symptoms commonly associated with other malignancies, including constitutional symptoms such as weight loss, tend to occur less frequently or may be absent. Perineal or rectal pain may only be present in 25.6% of patients. Hematuria, burning on ejaculation, and constitutional symptoms are a less common presentation (< 10% of patients).3,4 PSA levels typically do not rise and are found to be within normal limits. The lack of PSA elevation is related to the tumors nonepithelial origin and may contribute to a delay in diagnosis.2,4,5