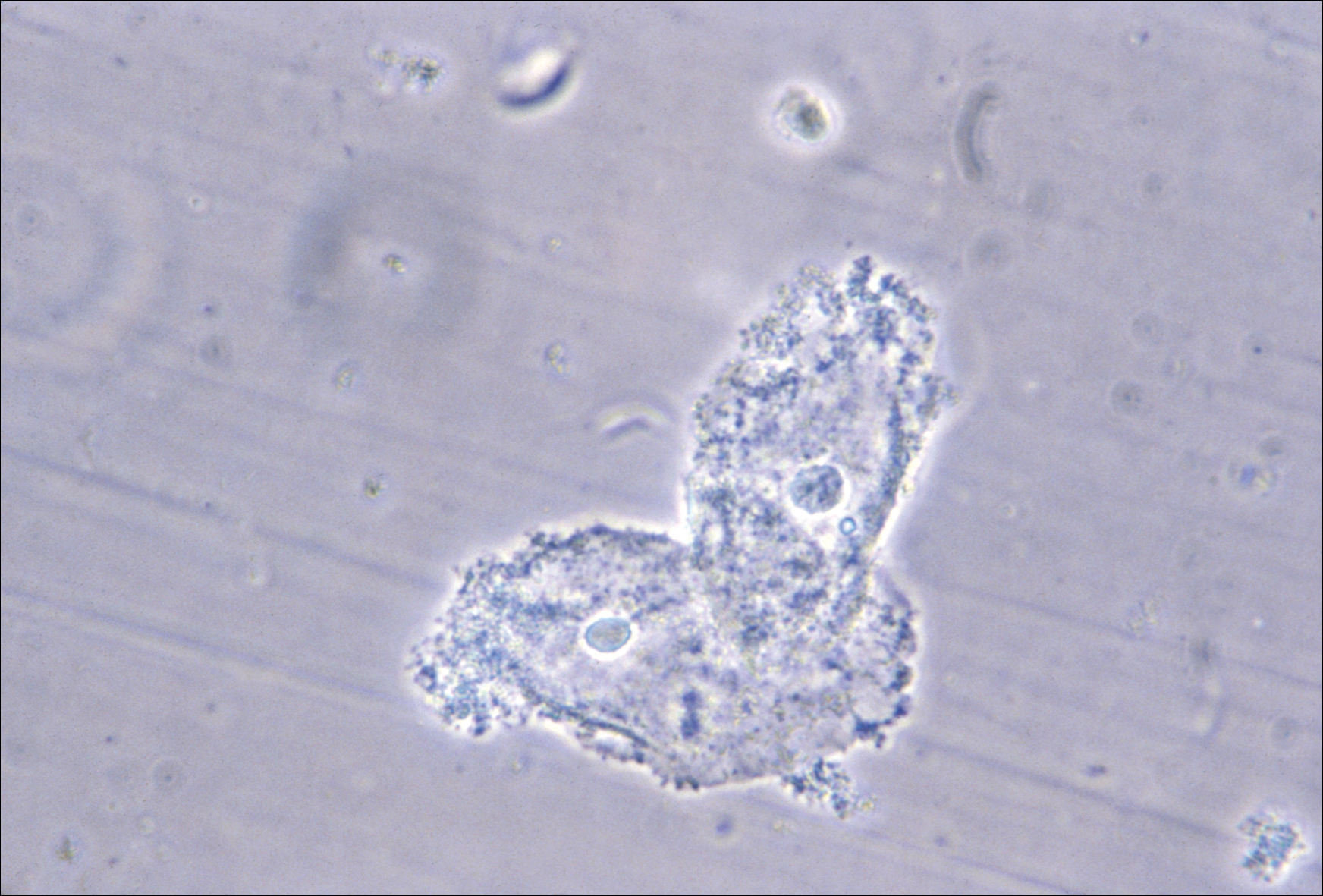
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is caused by a complex change in vaginal bacterial flora, with a reduction in lactobacilli (which help maintain an acidic environment) and an increase in anaerobic gram-negative organisms including Gardnerella vaginalis species and Bacteroides, Prevotella, and Mobiluncus genera. Infection with G vaginalis is thought to trigger a cascade of changes in vaginal flora that leads to BV.1
BV is present in 30% to 50% of sexually active women, and of these women 50% to 75% have an abnormal vaginal discharge, which is gray, thin, and homogeneous and may have a fishy odor.2 In addition to causing an abnormal vaginal discharge, BV is a cause of postpartum fever, posthysterectomy vaginal cuff cellulitis, and postabortion infection, and it increases the risk of acquiring HIV, herpes simplex type 2, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis infection.3
When using microscopy and the Amsel criteria, the diagnosis of BV is made when at least 3 of the following 4 criteria are present:
- homogeneous, thin, gray discharge
- vaginal pH >4.5
- positive whiff-amine test when applying a drop of 10% KOH to a sample of the vaginal discharge
- clue cells detected with microscopy on a saline wet mount.
If microscopy is not available, the Affirm VPIII test (BD Diagnostic Systems, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey) for DNA sequences of G vaginalis has high sensitivity and specificity.4 The OSOM BVBlue test (Sekisui Diagnostics, Lexington, Massachusetts), a Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments-waived point of service test, measures vaginal sialidase, which is produced by Gardnerella and other pathogens associated with BV.5 BV may be detected in routine cervical cytology testing and, if the patient is symptomatic, treatment is recommended.
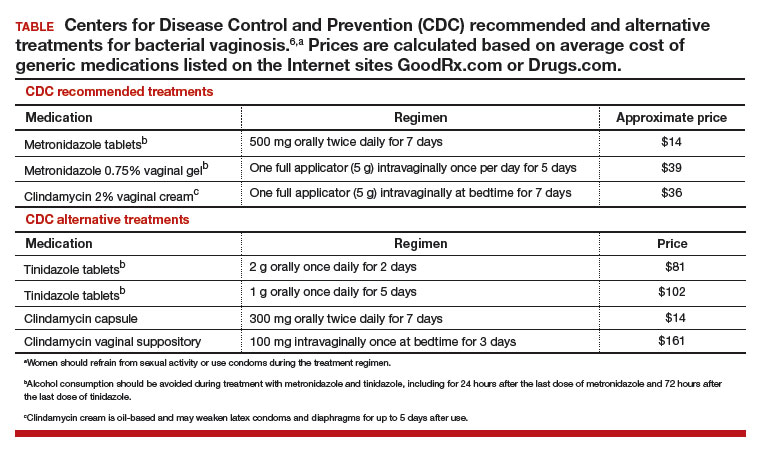
Initial treatment of BV. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has recommended 3 treatment regimens for BV and 4 alternative treatment options (TABLE).6 In addition to antimicrobial treatment, the CDC recommends that women with BV use condoms with sexual intercourse. The CDC also advises that clinicians should con-sider testing women with BV for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections.
Related article:
Successful treatment of chronic vaginitis
Treatment of recurrent BV
A major problem with BV is that, although initial treatment is successful in about 80% of cases, up to 50% of women will have a recurrence of BV within 12 months of initial treatment.2 Preliminary studies suggest that for women with 3 or more episodes of BV, the regimens below may be effective.
Regimen 1
Following the completion of a CDC-recommended treatment regimen (see TABLE), prescribe metronidazole vaginal gel 0.75%, one full applicator, twice weekly for 6 months.7
In a prospective randomized trial examining this regimen, following initial treatment with a 10-day metronidazole vaginal gel regimen 112 women were randomly assigned to chronic suppressive therapy with metronidazole vaginal gel 0.75%, one full applicator, twice weekly for 16 weeks or a placebo. During the treatment period, recurrent BV was diagnosed in 26% of the women taking metronidazole gel and 59% of the women taking placebo.7 This regimen may be complicated by secondary vaginal candidiasis, which may be treated with a vaginal or oral antifungal agent.
Regimen 2
Initiate a 21-day course of vaginal boric acid capsules 600 mg once daily at bedtime and simultaneously prescribe a standard CDC treatment regimen (see TABLE). At the completion of the vaginal boric acid treatment initiate metronidazole vaginal gel 0.75% twice weekly for 6 months.8
NOTE: Boric acid can cause death if consumed orally.9 Boric acid capsules should be stored securely to ensure that they are not accidentally taken orally. Boric acid poisoning may present with vomiting, fever, skin rash, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, metabolic acidosis, and renal failure.10 Boric acid should not be used by pregnant women because it is a teratogen.11
The bacterial organisms responsible for BV reside in a self-produced matrix, referred to as a biofilm, that protect the organisms from antimicrobial agents.12 Boric acid may prevent the formation of a biofilm and increase the effectiveness of anti-microbial treatment.
Regimen 3
Following the completion of a standard treatment regimen (see TABLE), prescribe oral metronidazole 2 g and fluconazole 150 mg administered once every month.13
In a randomized clinical trial, 310 female sex workers were randomly assigned to monthly treatment with oral metronidazole 2 g plus fluconazole 150 mg or placebo for up to 12 months.13 In the treatment and placebo groups episodes of BV were 199 and 326 per 100 person-years, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.55; 95% confidence interval, 0.49-0.63; P<.001). In Canada, a vaginal ovule containing both a high dose of metronidazole (500 mg) and nystatin (10,000 IU) is available and could be used intermittently to prevent recurrence.14
Treatment of partners
The CDC does not recommend treatment of the partners of women with BV because there are no definitive data to support such a recommendation. However, the 6 published clinical trials testing the utility of treating sex partners of women with BV have significant methodologic flaws, including underpowered studies and suboptimal antibiotic treatment regimens.15 Hence, whether partners should be treated remains an open question. Many experts believe that, in most cases, BV is a sexually transmitted disease.16,17 For women who have sex with women, the rate of BV concordance among partners is high. If one woman has diagnosed BV and symptoms are present in her partner, treatment of the partner is reasonable. For women with BV who have sex with men, sexual intercourse influences disease activity, and consistent use of condoms may reduce the rate of recurrence.18 Male circumcision may reduce the risk of BV in female partners.19
Related article:
Bacterial vaginosis: Meet patients' needs with effective diagnosis and treatment
Over-the-counter treatments
In women with BV it is thought that the vaginal administration of lactic acid can help restore the normal acidic pH of the vagina, encourage the growth of lactobacilli, and suppress the growth of the bacteria that cause BV.20 Many products containing lactic acid in a formulation for vaginal use are available (among them Luvena and Gynofit gel).
Lactobacilli play an important role in maintaining vaginal health. Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Lactobacillus reuteri are available for purchase as supplements for oral administration. It is thought that oral administration of lactobacilli can help improve the vaginal microbiome. In one clinical trial, 125 women with BV were randomly assigned to receive the combination of 1 week of metronidazole plus oral Lactobacillus twice daily for 30 days or metronidazole plus placebo.21 Resolution of symptoms was reported as 88% and 40% in the metronidazole-lactobacilli and metronidazole-placebo groups, respectively.21 By contrast, one systematic review of probiotic treatment of BV concluded that there is insufficient evidence to recommend for or against probiotic treatment of BV.22 Patients with recurrent BV commonly report that they believe a probiotic was helpful in resolving their symptoms.
On the horizon
In one trial, a single 2-g oral dose of secnidazole was as effective as a 7-day course of oral metronidazole 500 mg twice daily.23 In a small dose-finding study, a single dose of either secnidazole 1 g or 2 g was equally effective in treating BV.24 An effective single-dose treatment of BV would likely improve patient adherence with therapy. Symbiomix is preparing for FDA review of this medication (secnidazole, Solosec) for use in the United States.
BV is a prevalent problem and often adversely impacts a woman's quality of life and love relationships. BV recurrence is very common. Many women report that their BV was resistant to intermittet treatment and recurred, repetitively over many years. The 3 treatment options presented in this editorial may help to suppress the recurrence rate and improve symptoms.
Share your thoughts! Send your Letter to the Editor to rbarbieri@frontlinemedcom.com. Please include your name and the city and state in which you practice.