In recent decades the practice of medicine has drifted away from the performance of a physical examination during most patient encounters and evolved toward the more intensive use of history, imaging, and laboratory studies to guide management decisions. For example, it is common for a woman to present to an emergency department with abdominal or pelvic pain and undergo a computerized tomography scan before an abdominal and pelvic examination is performed. Some authorities believe that the trend to reduce the importance of the physical examination has gone way too far and resulted in a reduction in the quality of health care.1,2
Many skin diseases only can be diagnosed by having the patient disrobe and examining the skin. Gynecologists are uniquely positioned to diagnose important skin diseases because, while performing a reproductive health examination, they may be the first clinicians to directly examine the anogenital area and inner thighs. Skin diseases that are prevalent and can be diagnosed while performing an examination of the anogenital region include lichen sclerosus (LS) and hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). The prevalence of each of these conditions is in the range of 1% to 4% of women.3–5
Failure to examine the anogenital area and insufficient attention to the early signs of LS and HS may result in a long delay in the diagnosis.6 In 1 survey, of 517 patients with HS, there was a 7-year interval between the onset of the disease and the diagnosis by a clinician.7 Delay in diagnosis results in increased scarring, which makes it more difficult to effectively treat the disease. In this editorial, I will focus on the pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment of HS.
Diagnosis, presentation, and staging
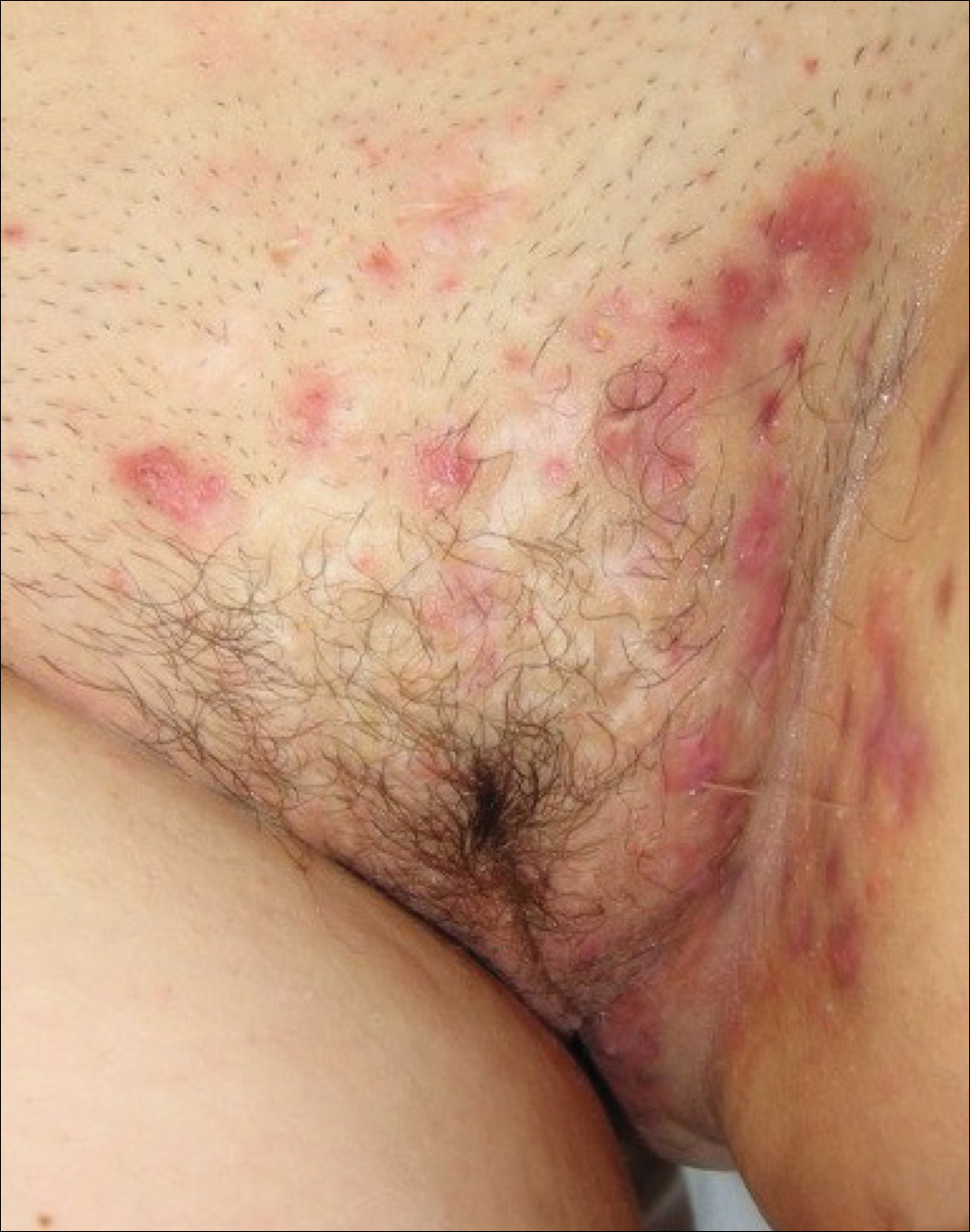
Hidradenitis suppurativa (from the Greek, hidros means sweat and aden means glands) is a painful, chronic, relapsing, inflammatory skin disorder affecting the follicular unit. It is manifested by nodules, pustules, sinus tracts, and scars, usually in intertriginous areas. The diagnosis is made by history and physical examination. The 3 cardinal features of HS are 1) deep-seated nodules, comedones, and fibrosis; 2) typical anatomic location of the lesions in the axillae, inguinocrural, and anogenital regions, and 3) chronic relapsing course.8
Disease severity is often assessed using the Hurley staging system:
- stage I: abscess formation without sinus tracts or scarring (FIGURE)
- stage II: recurrent abscesses with tract formation and scarring, widely separated lesions
- stage III: diffuse or near-diffuse involvement or multiple interconnected tracts and abscesses.
In one report, stage I, II, and III disease was diagnosed in 65%, 31%, and 4% of cases, respectively, indicating that most HS is diagnosed instage I and suitable for treatment by a gynecologist.9
HS typically presents after puberty and women are more commonly affected than men. In one case series including 232 women with HS the regions most commonly affected were: axillae, inguinofemoral, urogenital, and buttocks in 79%, 77%, 51%, and 40% of cases, respectively.10 Risk factors for HS include obesity, cigarette smoking, tight fitting clothing, and chronic friction across the affected skin area.5
Pathogenesis
The pathophysiology of HS is thought to begin with occlusion of the follicle, resulting in follicle rupture deep in the dermis, thereby triggering inflammation, bacterial infection, and scarring. Dermal areas affected by HS have high concentrations of cytokines, including tumor necrosis factor (TNF)–alpha, interleukin (IL)-1-beta, IL-23, and IL-32.11,12 Once HS becomes an established process, it is difficult to treat because the dermal inflammatory process and scarring provides a microenvironment that facilitates disease progression. Hence early detection and treatment may result in optimal long-term outcomes.