In 57 women who underwent this procedure, the mean operative time was 127 minutes; average estimated blood loss was 267 mL.40 Overall, laparoscopy with minilaparotomy was found to be a less technically difficult technique for laparoscopic myomectomy; allowed better closure of the uterine defect; and might have required less time to perform.3
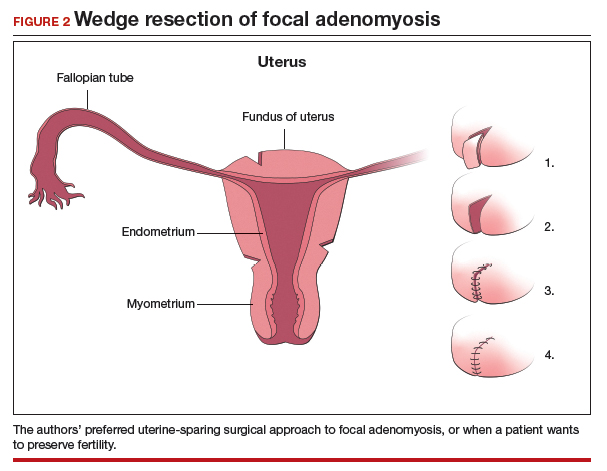
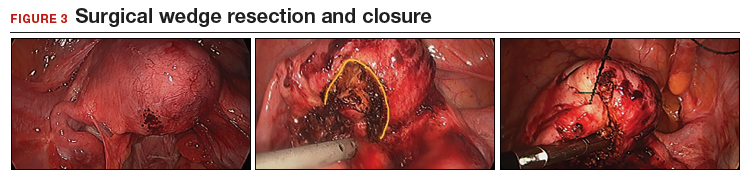
We therefore advocate video laparoscopic wedge resection with or without robotic assistance, aided by minilaparotomy when necessary for safe removal of larger adenomyomas, as the preferred uterine-sparing surgical approach for focal adenomyosis or when the patient wants to preserve fertility (FIGURE 2). We think that this technique allows focal adenomyosis to be treated by wedge resection of the diseased myometrium, with subsequent closure of the remaining myometrial defect using a barbed V-Loc (Medtronic, Minneapolis, Minnesota) delayed absorbable suture in layers (FIGURE 3). Minilaparotomy can be utilized when indicated to aid removal of the resected myometrial specimen.
In our extensive experience, we have found that this technique provides significant relief of symptoms and improvements in fertility outcomes while minimizing surgical morbidity.
CASE Resolved
The patient underwent successful wedge resection of her adenomyosis by laparoscopy. She experienced nearly complete resolution of her symptoms of dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, and pelvic pain. She retained good uterine integrity. Three years later, she and her husband became parents when she delivered their first child by cesarean delivery at full term. After she completed childbearing, she ultimately opted for minimally invasive hysterectomy.
The authors would like to acknowledge Mailinh Vu, MD, Fellow at Camran Nezhat Institute, for reviewing and editing this article.