Posterior compartment repairs
Like with the anterior compartment, opinions differ as to the site of posterior compartment prolapse. Midline, lateral, distal, and site-specific defects and surgical approaches have been described. Research suggests that there is no benefit to the use of mesh in the posterior compartment.7 It is very important to recognize that over-plication of the posterior compartment can lead to narrowing/stricture and dyspareunia. Therefore, monitor vaginal caliber throughout repair of the posterior compartment.
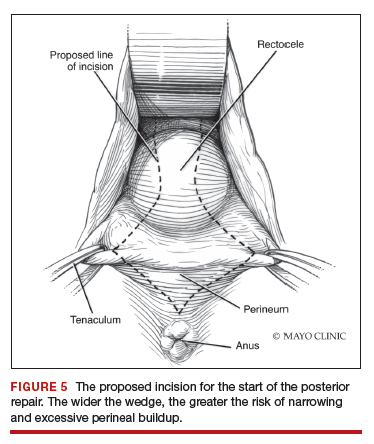
Although we believe that a midline defect in the endopelvic fascia is primarily responsible for rectoceles, we also appreciate that the fascia must be reconstructed all the way to the perineal body and that narrowing the genital hiatus is very important and often underappreciated (FIGURE 5). Thus, perineal reconstruction is universally performed. I will emphasize again that reconstruction must be performed while also monitoring vaginal caliber. If it is too tight with the patient under anesthesia, it will be too tight when the patient recovers. Avoidance is the best option. If the patient does not desire a functional vagina (eg, an elderly patient), then narrowing is a desired goal.
Perineal reconstruction technique and tips for success
A retractor at 12 o’clock to support the apex and anterior wall can be helpful for visualization in the posterior compartment. We start with a v-shaped incision on the perineum. The width is determined by how much you want to build up the perineum and narrow the vagina (the wider the incision, the more building up of the perineal body and vaginal narrowing). A strip of epithelium is then mobilized in the midline (be careful not to excise too much). This dissection is carried all the way up the midline to just short of the tied apical suspension sutures at the posterior vaginal apex. The posterior dissection tends to be the most vascular in my experience.
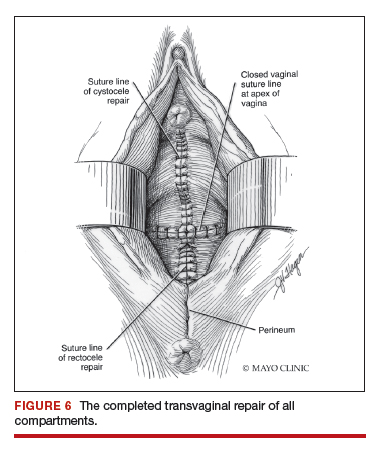
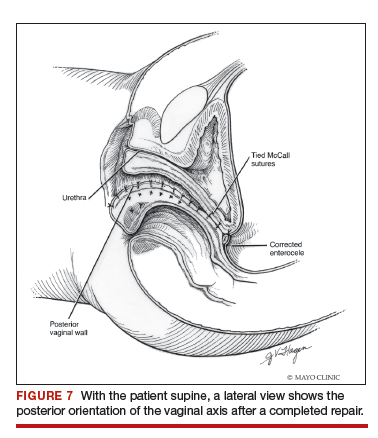
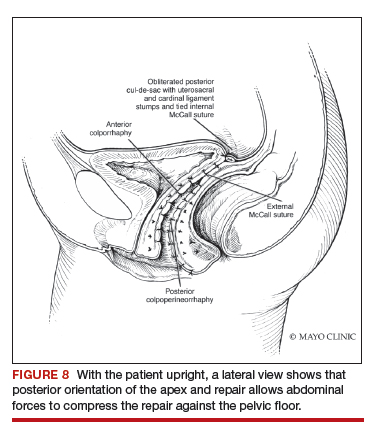
Utilize cautery to obtain hemostasis along your dissection margins while protecting the underlying rectum. We have not found it necessary to dissect the posterior epithelium off the underlying fascia (that is an option at this point, however, if you feel more comfortable doing this). With an index finger in the vagina, compressing the rectum posteriorly, interrupted 1-0 polyglactin suture is placed through the epithelium and underlying fascia (avoiding the rectum) on one side, then the other, and then tied. The next sutures are placed utilizing the same technique, and the caliber of the vagina is noted with the placement of each suture (if it is too tight, then remove and replace the suture and recheck). It is important to realize you want to plicate the fascia in the midline and not perform an aggressive levatorplasty that could lead to muscle pain. Additionally, each suture should get the same purchase of tissue on each side, and the spacing of each suture should be uniform, like rungs on a ladder. Ultimately, the repair is carried down to the hymenal ring. At this point, the perineal reconstruction is performed, plicating the perineal body in the midline with deeper horizontal sutures and then closing the perineal skin with interrupted or subcuticular sutures (FIGURE 6). Completion of these repairs should orient the vagina toward the hollow of the sacrum (FIGURE 7), allowing downward forces to compress the vaginal supports posteriorly onto the pelvic floor instead of forcing it out the vaginal lumen (FIGURE 8).
Our patients generally stay in the hospital overnight, and we place a vaginal pack to provide topical pressure throughout the vagina overnight. We tell patients no lifting more than 15 lb and no intercourse for 6 weeks. While we do not tend to use hydrodissection in our repairs, it is a perfectly acceptable option.
Continue to: Commit to knowledge of native tissue techniques...