Ms. L, age 37, presents to psychiatric emergency services with command auditory hallucinations, ideas of reference, and suicidal ideation.
Ms. L has a 22-year history of schizophrenia. Additionally, she has a history of cocaine use disorder (in remission for 12 years), cannabis use disorder (in remission for 6 months), type 2 diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. Her psychotic symptoms are well controlled on a regimen of clozapine, 700 mg/d, and paliperidone palmitate, 156 mg/month. Ms. L says she has been adherent to these medications, and this is confirmed by the assertive community treatment (ACT) team member who administers the medications at Ms. L’s home each day.
On interview, Ms. L reports smoking cannabis each day for the past month and using $400 worth of cocaine over 2 days. She is experiencing intense guilt over these relapses and is admitted to the inpatient adult psychiatry unit. On admission, Ms. L’s clozapine and norclozapine trough levels (drawn approximately 12 hours after last administration documented by the ACT member) are 300 and 275 ng/mL, respectively. Generally, clozapine levels >350 to 420 ng/mL are considered therapeutic, and a clozapine-to-norclozapine ratio of 2:1 is desirable for maximum efficacy and tolerability. Because Ms. L’s clozapine level is <350 and her ratio is approximately 1:1, her clozapine treatment is subtherapeutic.
Because Ms. L has a history of documented adherence to and benefit from her current medication regimen, no changes are made during her 3-week hospital stay. She notices a gradual reduction in auditory hallucinations, no longer wants to harm herself, and is motivated to regain sobriety.
At the time of discharge, Ms. L’s clozapine and norclozapine trough levels are 550 and 250 ng/mL, respectively, which indicates a more favorable clozapine-to-norclozapine ratio of approximately 2:1 and a clozapine level greater than the recommended minimum threshold of 350 ng/mL. While cocaine ingestion presumably played a role in her acute decompensation, the treatment team determined that Ms. L’s relapse to cannabis use likely contributed to low clozapine levels by induction of cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A2, and subsequently led to the delayed recovery of symptom control.1
The use of illicit substances is a widespread, growing problem. According to the 2017 National Survey on Drug Use and Health, 11.5% of Americans age ≥12 had used an illicit substance (ie, use of marijuana, cocaine, heroin, hallucinogens, inhalants, or methamphetamine, or misuse of prescription psychotherapeutics) in the past month.2 While illicit substance use is of particular public health interest due to a known increase in mortality and health care spending, there has been little discussion of the impact of illicit drug use on concurrent pharmacologic therapy. Just as prescription medications have pharmacokinetic drug–drug interactions with each other, so do illicit substances, though far less is known about their impact on the treatment of medical conditions.
Pharmacokinetic interactions
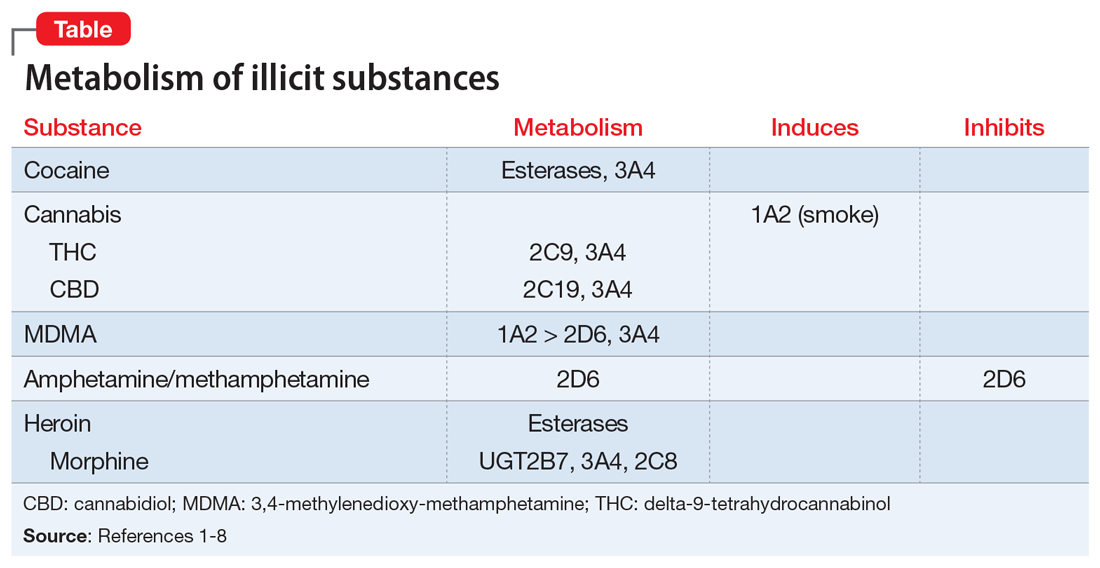
Key pharmacokinetic interactions have been reported with cocaine, marijuana, amphetamines, and opioids. The Table1-8 summarizes the metabolism of illicit substances.
Continue to: Cocaine