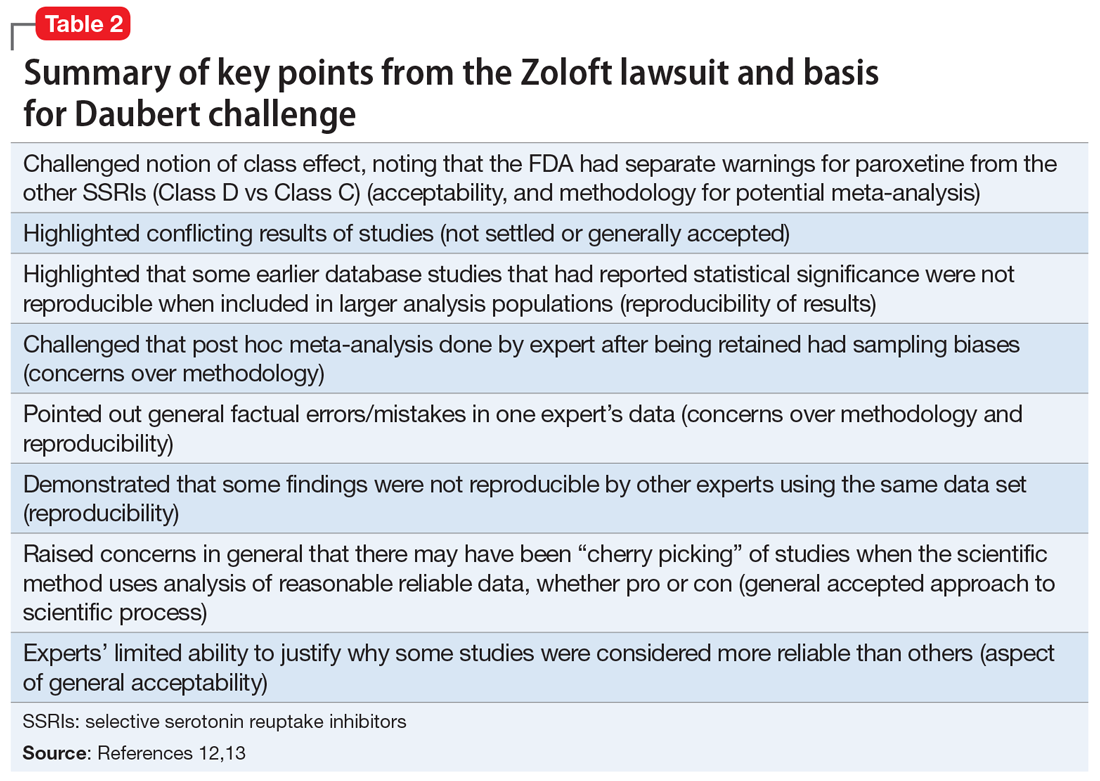
Many of the more than 300 federal claims were united in a multi-district litigation (MDL) suit under the United States District Court of Eastern Pennsylvania (MDL 2342). Pfizer issued Daubert challenges (efforts to exclude the introduction of “junk science” into the courtroom) against the plaintiffs’ experts’ scientific methods and results.12,13 The plaintiffs (those suing Pfizer) had to prove that the medications caused the negative outcome, not that they were merely temporally associated. Subsequently, 2 plaintiff experts—a PharmD and a biostatistician—were removed. Pfizer successfully challenged the methodological soundness of the plaintiffs’ experts’ testimony (Table 212,13), and the case was dismissed. In general, the courts identified the Bradford Hill criteria as often being important (though not definitive) methodology for determining causation (Table 312,13).
A concept raised in prior psychotropic lawsuits was the “learned intermediary doctrine,” in which pharmaceutical companies stated that once a risk is known, it is the responsibility of the prescribing physician to assess risks vs benefits and inform the patient.8 Many aspects of the larger class action lawsuits related to failure of the company to do adequate research to identify risks and appropriately inform the public and the medical community of these risks.14
Challenges in interpreting the literature
Some of the difficulties in interpreting the literature on the association of antidepressants and birth defects can be seen in a 2020 study by Anderson et al.15 This study was published in JAMA Psychiatry, received widespread coverage in the media, and was discussed on the CDC’s website.16 Anderson et al15 compared a large cohort of 30,630 infants with birth defects from the multicenter case-control National Birth Defects Prevention Study with 11,478 randomly selected controls with no defects. Three primary study groups were women whose pregnancies resulted in:
- birth defects with no antidepressant exposure (n = 28,719)
- birth defects with exposure to an antidepressant (n = 1,911)
- no birth defect control group (n = 10,886 no antidepressant exposure, n = 592 antidepressant exposure).
This study reported there were “some associations between maternal antidepressant use and specific birth defects” and “Venlafaxine was associated with more birth defects than other antidepressants, which needs confirmation.”15 However, in an accompanying editorial, Wisner et al17 discussed potential problems and limitations with this study and research of this nature in general (Table 417). In addition, Anderson et al15 used certain “controversial” statistical practices.18 For example, “[T]o align with American Statistical Association guidelines to consider effect sizes when interpreting results instead of statistical significance, we noted associations as meaningfully elevated if [adjusted odds ratios] were 2.0 or greater and lower confidence interval bounds were 0.8 or greater.”15
Those who read only abstracts or news stories may believe this study of >40,000 participants included a large number of women who were receiving venlafaxine. However, the number of pregnant women who were prescribed venlafaxine was actually very small—112 who took venlafaxine experienced a birth defect. In addition, the authors noted “Venlafaxine was associated with many of the same defects across the samples (data not shown).”15 As discussed above, historically one of the areas the courts have considered was whether or not appropriate methodology was applied, and whether the results could be replicated with the data provided.
Continue to: Further, new studies...