Commentary
Hidradenitis Suppurativa Scoring Systems: Can We Choose Just One?
Interest in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has exploded in the last few years. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the MeSH term...
From the Department of Internal Medicine, Division of Dermatology, David Geffen School of Medicine, University of California, Los Angeles.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Scott D. Worswick, MD, Division of Dermatology, David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, 200 Medical Plaza, Ste 450, Los Angeles, CA 90095 (sworswick@mednet.ucla.edu).

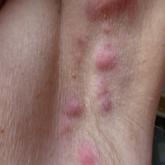
The clinical suspicion of a thrombotic event on the dorsal feet, which was confirmed histologically, and the persistently positive antiphospholipid (aPL) antibody titers helped to establish the diagnosis of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) in the setting of RA. The dose of prednisone was increased from 10 mg daily on admission to 40 mg daily. The patient was started on enoxaparin 60 mg subcutaneously twice daily at initial presentation and was bridged to oral warfarin 2 mg daily after the diagnosis of APS was established. Oral doxycycline 100 mg twice daily was started for wound infection. The ulcerations gradually improved over the course of her 7-day hospitalization. She was continued on prednisone, hydroxychloroquine, and warfarin as an outpatient and has had no recurrence of lesions after 3 years of follow-up on this regimen.
Antiphospholipid syndrome is an autoimmune condition defined by a venous and/or arterial thrombotic event and/or pregnancy morbidity in the presence of persistently elevated aPL antibody titers. The most frequently detected subgroups of aPL are anticardiolipin (aCL) antibodies, anti-β2-glycoprotein I antibodies, and lupus anticoagulants.1 Primary APS occurs as an isolated entity, whereas secondary APS occurs in the setting of a preexisting autoimmune disease, infection, malignancy, or medication.2 The diagnostic criteria for APS requires positive aPL titers at least 12 weeks apart and a clinically confirmed thrombotic event or pregnancy morbidity.3
About one-third to half of patients with APS exhibit cutaneous manifestations.4,5 Livedo reticularis is most commonly observed and represents the first clinical sign of APS in 17.5% of cases.6 Cutaneous findings of APS also include anetoderma, cutaneous ulceration and necrosis, necrotizing vasculitis, livedoid vasculitis, thrombophlebitis, purpura, ecchymoses, painful skin nodules, and subungual hemorrhages.7 The various cutaneous manifestations of APS are associated with a range of histopathologic findings, but noninflammatory thrombosis in small arteries and/or veins in the dermis and subcutaneous fat tissue is the most common histologic feature.4 Our patient exhibited cutaneous ulceration and necrosis, and biopsy clearly showed the presence of vasculitis and fibrin thrombi within postcapillary venules. These findings along with the persistently elevated β2-glycoprotein I IgA solidified the diagnosis of APS.
The most common cutaneous manifestations of RA are nodules (32%), Raynaud phenomenon (10%), and vasculitis (3%).8 The mean prevalence of aPL antibodies in patients with RA is 28%, though reports range from 5% to 75%.1 The presence of aPL or aCL does not predict the development of thrombosis and/or thrombocytopenia in RA patients9,10; however, aCL antibodies in RA patients are associated with a higher risk for developing rheumatoid nodules. It is hypothesized that the majority of aCL antibodies identified in RA patients have different specificities than those identified in other diseases that are associated with thrombotic events.1
Anticoagulation has been proven to decrease the risk for recurrent thrombotic events in patients with APS.11 Patients should discontinue the use of estrogen-containing oral contraceptives; avoid smoking cigarettes; and treat hypertension, hyperlipidemia, and diabetes mellitus, if present. The type and duration of anticoagulation therapy, especially for the treatment of the cutaneous manifestations of APS, is less well defined. Antiplatelet therapies such as low-dose aspirin or dipyridamole often are used for less severe cutaneous manifestations such as livedoid vasculopathy. Warfarin with a target international normalized ratio of 2.0 to 3.0 is most commonly used following major thrombotic events, including cutaneous necrosis and digital gangrene. The role of corticosteroids and immunosuppressants is unclear; one study showed that these therapies did not prevent further thrombotic events in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus.4
Although aPL antibodies are most prevalent in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, an estimated 28% of patients with RA have elevated aPL titers. The aPL antibodies recognized in RA patients are thought to have a different specificity than those recognized in other APS-associated diseases because elevated aPL antibody titers are not associated with an increased incidence of thrombotic events in RA patients; however, larger studies are needed to clarify this phenomenon. It remains to be determined if this case of APS and RA represents a coincidence or a true disease association, but the recognition of the cutaneous and histological features of APS is crucial for establishing a diagnosis and initiating anticoagulation therapy to prevent further morbidity and mortality.

Interest in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) has exploded in the last few years. A PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the MeSH term...
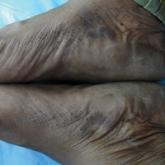
A 43-year-old woman with recently diagnosed diabetes mellitus and a history of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura on chronic oral steroids...
RASopathies, a class of developmental disorders, are caused by mutations in genes that encode protein components of the RAS/mitogen-activated...
