Case Reports
Rowell Syndrome: Targeting a True Definition
Ever since a rare syndrome of lupus erythematosus (LE) presenting with erythema multiforme (EM)–like lesions was described in 1963, clinicians...
From the Department of Dermatology and the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Alina G. Bridges, DO, Department of Dermatology, Mayo Clinic, 200 First St SW, Rochester, MN 55905 (bridges.alina@mayo.edu).

An association between steatocystoma multiplex (SCM) and eruptive vellus hair cysts (EVHCs) has been recognized. Steatocystoma multiplex and EVHC have similar clinical features but distinctive histologic features. Rare cases of co-occurrence of these conditions have been known to occur on the trunk and the forehead. We report a rare case of the simultaneous occurrence of SCM, EVHC, and trichofolliculomas localized to the forehead.
Practice Points
An association between steatocystoma multiplex (SCM) and eruptive vellus hair cysts (EVHCs) has been recognized. They are related conditions representing nevoid malformations of the pilosebaceous junctions1-10 that have similar clinical features but distinctive histologic features. Both conditions most commonly involve the anterior aspect of the chest. Six cases of a rare facial variant of SCM have been reported,11-16 3 involving lesions limited to the forehead.13-15 Two patients with a rare facial variant of EVHC also have been reported.17 The development of separate lesions of SCM and EVHC on the trunk can uncommonly occur.5,6,10 One case of SCM and EVHC on the forehead has been described.3 Other types of benign follicular neoplasms simultaneously developing in association with SCM or EVHC also are rare. The simultaneous occurrence of multiple trichoblastomas, trichoepitheliomas, and SCM on the face and trunk has been reported in 1 case.18 Milia, SCM, and EVHC on the face and trunk have been reported in 1 family.4 A report of facial steatocystoma associated with a pilar cyst and bilateral preauricular sinus also has occurred in 1 patient.19 Here, we report the simultaneous occurrence of SCM, EVHC, and trichofolliculomas localized to the forehead.
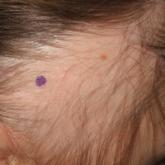
A 37-year-old man had an increasing number of flesh-colored to yellow papules on the forehead that had been present since puberty. Although the lesions were asymptomatic, some had recently become tender, which led him to seek medical care. There was no history of trauma, burns, irradiation, or application of topical agents to the area or use of eyeglasses or goggles. The patient’s father had similar lesions limited to the forehead, which developed during adolescence.
On evaluation at our clinic, skin examination revealed 16 discrete, 0.3- to 1-cm, flesh-colored, yellow to blue, mobile, smooth papules, as well as flesh-colored papules with a central black punctum, on the forehead (Figure 1). Similar lesions were not present on the rest of the face; around the ears; or on the scalp, neck, chest, back, abdomen, genitalia, buttocks, palms, soles, axillae, arms, or legs. There were no nail abnormalities.
Multiple 3-, 4-, and 6-mm punch and excisional biopsies were performed to remove all 16 lesions on the forehead. Histologic examination revealed a collapsed cystic structure in the mid dermis in 10 lesions. The cysts were lined with a squamous epithelium without a granular layer but with an eosinophilic corrugated lining, and the cyst cavity contained scant homogeneous eosinophilic secretion. Mature sebaceous glands were adjacent to the outer portion of the cyst wall. These histologic findings were consistent with SCM (Figure 2).
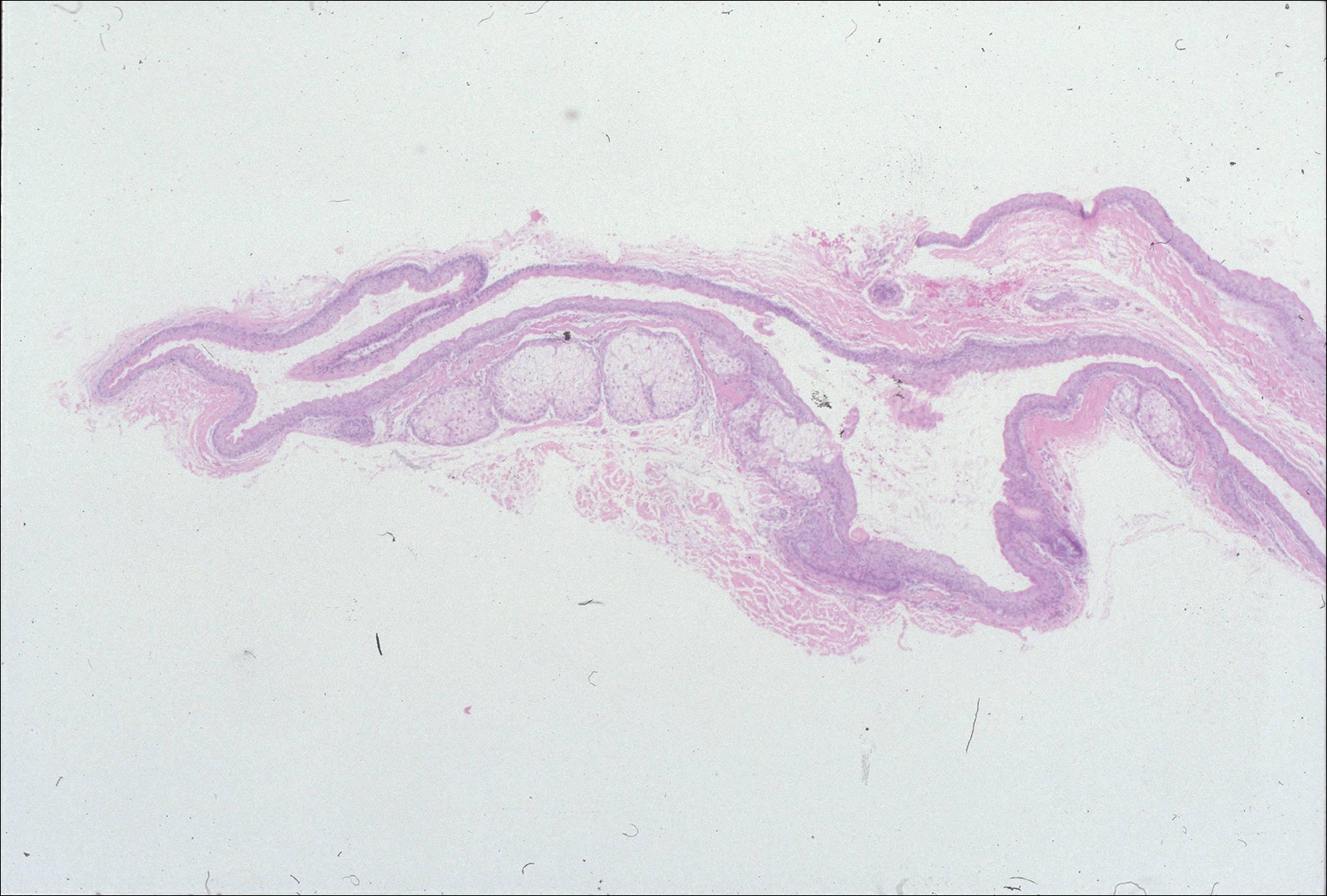
Figure 2. Photomicrograph of a steatocystoma multiplex lesion demonstrated a collapsed cystic space with parallel infoldings of the cyst wall. The cyst wall was composed of a squamous epithelium without a granular layer but with an eosinophilic corrugated lining. The cyst cavity contained scant homogeneous eosinophilic secretion. Mature sebaceous lobules emanated from the cyst wall (H&E, original magnification ×10).
In 3 lesions, histologic examination revealed a cystic structure lined by a few layers of stratified squamous epithelium in the mid dermis. The cyst cavity contained numerous small vellus hairs and laminated keratin. These histologic findings were consistent with EVHC (Figure 3).
In the other 3 lesions, histologic examination revealed a dilated central cystic cavity filled with laminated keratin in the mid dermis. Multiple small follicles arose from the cysts and showed differentiation toward germinative epithelium. The surrounding stroma was fibrotic and contained a patchy lymphocytic infiltrate. These histologic findings were consistent with trichofolliculomas (Figure 4).
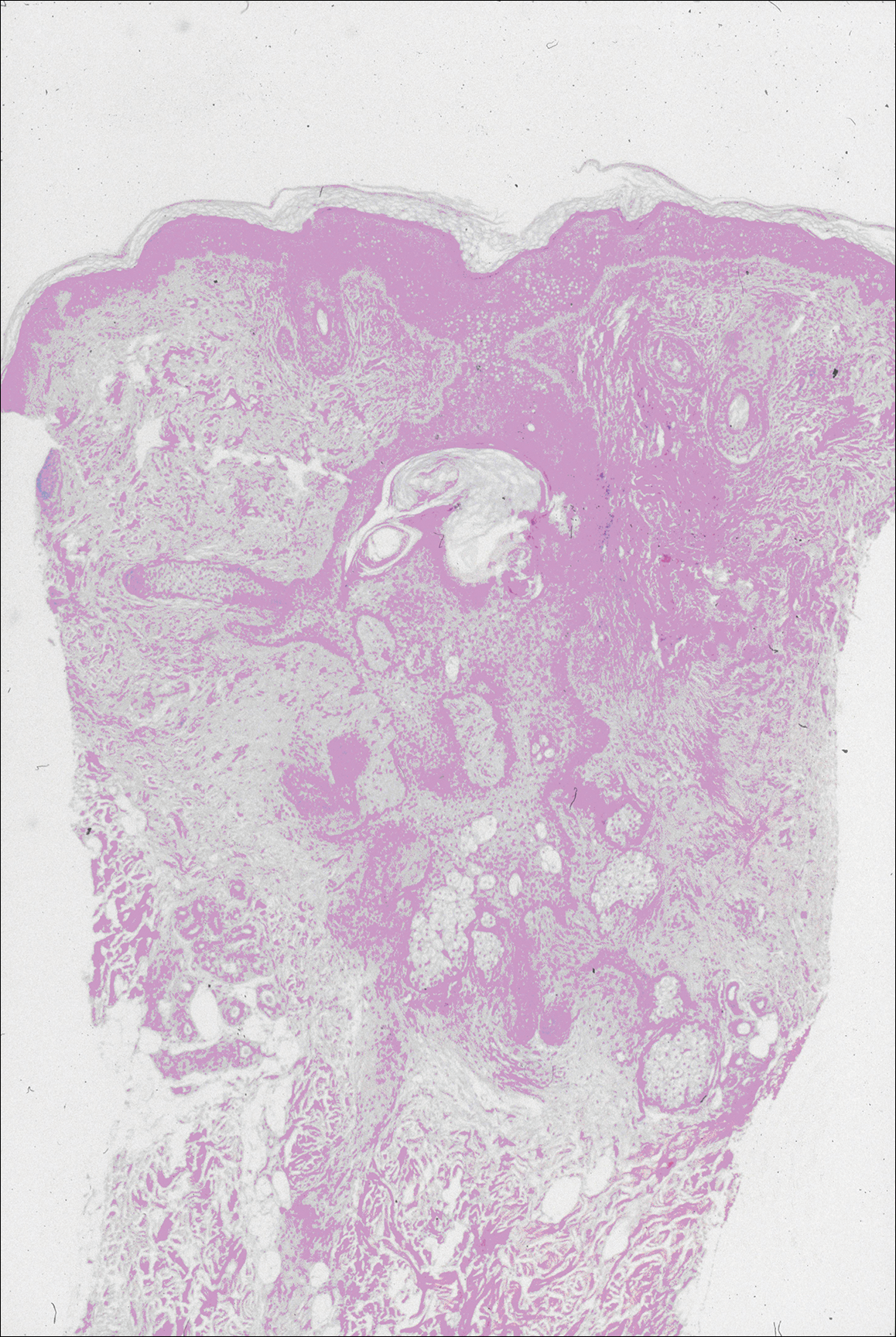
Figure 4. Photomicrograph of a trichofolliculoma demonstrated a central dilated primary follicle that was contiguous with the surface epidermis and contained laminated keratin. Multiple small secondary follicles arose from the primary follicle. These secondary follicles showed differentiation toward germinative epithelium and hair bulb and papilla formation. The stroma was fibrotic (H&E, original magnification ×10).

Ever since a rare syndrome of lupus erythematosus (LE) presenting with erythema multiforme (EM)–like lesions was described in 1963, clinicians...