Case Reports
Muckle-Wells Syndrome in the Setting of Basal Cell Nevus Syndrome
Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare disorder inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion that belongs to a group of hereditary periodic fever...
Dr. Shariff is from the University of New Mexico School of Medicine, Albuquerque. Dr. Hillerson is from the University of Kentucky Hospital, Lexington. Dr. Ross is from the University of Texas Medical Branch, Galveston. Dr. Ayala-Pena is from the University of Utah School of Medicine, Salt Lake City.
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Correspondence: Dustin Hillerson, MD, 900 S Limestone St, CTW 326, Lexington, KY 40536-0200 (dustin.hillerson@me.com).

Practice Points
To the Editor:
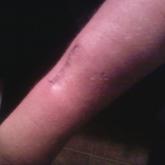
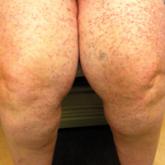
A 22-year-old obese man with untreated mild asthma diagnosed in childhood presented to the emergency department with cheilitis (Figure 1); conjunctivitis; and painful desquamation of the oral mucosa, penis (Figure 2), and perirectal area (Figure 3). Physical examination was notable for palpebral conjunctiva; mucosal involvement with stomatitis (Figure 1B); and isolated 0.5- to 2-cm erosions and ulcerations with positive Nikolsky sign of the scrotum (Figure 2), trunk, back, and arms and legs. Some areas had evidence of hemorrhagic crust, flaccid bullae, and denudation. Few scant targetoid lesions and dusky red macules on the trunk, face, palms, and soles also were present.
One week prior to presentation he had an episode of diarrhea and dyspnea with symptoms of mild heat stroke after working outdoors, and he self-treated with ibuprofen, which he had taken intermittently for years. He was subsequently seen at an outpatient clinic and was prescribed an albuterol inhaler for previously untreated childhood asthma. The patient stated that he inhaled 2 puffs every 6 hours for a total of 3 treatments. Shortly after the last dose, he noticed a tingling sensation of the oral mucosa that developed into a painful 2-cm bullous ulcer. Over the next 3 days, he developed several more oral ulcers and erosions. Three days before admission he developed dysuria and tense bullae at the glans penis. After admission, he developed cheilitis, conjunctivitis, dysuria, odynophagia, and dysphagia to solids. One day after admission, the patient had the onset of systemic symptoms, including cough with worsening dyspnea, fever, chills, hemoptysis, epistaxis, nausea, diarrhea, loss of appetite, joint pain, and myalgia. Review of systems was otherwise negative. A radiograph was performed at admission and was notable for mild atelectasis but was otherwise normal. The chest radiograph was negative for signs of perihilar lymphadenopathy, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or lobar infiltrates suggestive of bacterial pneumonia. It also did not show signs of patchy opacities or air bronchograms suggestive of an interstitial pneumonia. On admission, he was started on acyclovir, fluconazole, methylprednisolone, nystatin, pantoprazole, acetaminophen, topical bacitracin, oxycodone, and topical silver nitrate.
At the time of admission our patient was afebrile with a normal heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate. However, he was hypoxic, with a pulse oximetry of 86% on room air and 94% on 40% fraction of inspired oxygen. Complete blood cell count, electrolytes, and liver function tests were all within reference range. Urinalysis revealed evidence of scant red blood cells without pyuria, and the erythrocyte sedimentation rate and creatine kinase level were both elevated. Two blood cultures; sputum cultures; and polymerase chain reaction for Mycoplasma pneumoniae, herpes simplex virus, varicella-zoster virus, cytomegalovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus were negative. Human immunodeficiency virus panel, antinuclear antibody screen, and hepatitis B and C panels were all negative. Four punch biopsies were obtained showing full-thickness epidermal necrosis with neutrophils, few dyskeratotic cells, and sparse inflammatory infiltrate compatible with Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS).

Muckle-Wells syndrome (MWS) is a rare disorder inherited in an autosomal-dominant fashion that belongs to a group of hereditary periodic fever...
The mastocytoses comprise a group of proliferative stem cell disorders defined by the abnormal accumulation of mast cells (MCs) in the skin or...
