Photolichenoid dermatitis is an uncommon eruptive dermatitis of variable clinical presentation. It has a histopathologic pattern of lichenoid inflammation and is best characterized as a photoallergic reaction.1 Photolichenoid dermatitis was first described in 1954 in association with the use of quinidine in the treatment of malaria.2 Subsequently, it has been associated with various medications, including trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, azithromycin, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.1,2 Photolichenoid dermatitis has been documented in patients with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) with variable clinical presentations. Photolichenoid dermatitis in patients with HIV has been described both with and without an associated photosensitizing systemic agent, suggesting that HIV infection is an independent risk factor for the development of this eruption in patients with HIV.3-6
Case Report
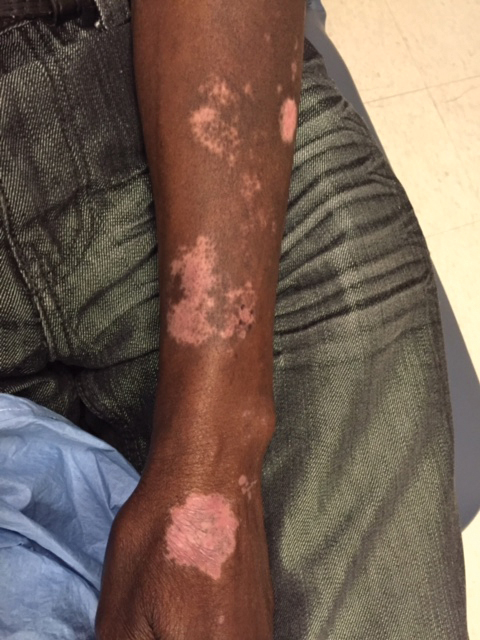
A 62-year-old African man presented for evaluation of asymptomatic hypopigmented and depigmented patches in a photodistributed pattern. The eruption began the preceding summer when he noted a pink patch on the right side of the forehead. It progressed over 2 months to involve the face, ears, neck, and arms. His medical history was negative. The only medication he was taking was hydroxychloroquine, which was prescribed by another dermatologist when the patient first developed the eruption. The patient was unsure of the indication for the medication and admitted to poor compliance. A review of systems was negative. There was no personal or family history of autoimmune disease. A detailed sexual history and illicit drug history were not obtained. Physical examination revealed hypopigmented and depigmented patches, some with overlying erythema and collarettes of fine scale. The patches were photodistributed on the face, conchal bowls, neck, dorsal aspect of the hands, and extensor forearms (Figures 1 and 2). Macules of repigmentation were noted within some of the patches. There also were large hyperpigmented patches with peripheral hypopigmentation on the legs.
A punch biopsy taken from the left posterior neck revealed a patchy bandlike lymphocytic infiltrate in the superficial dermis with lymphocytes present at the dermoepidermal junction and scattered dyskeratotic keratinocytes extending into the mid spinous layer (Figure 3). Histopathologic findings were consistent with photolichenoid dermatitis.
Laboratory workup revealed a normal complete blood cell count and complete metabolic panel. Other negative results included antinuclear antibody, anti-Ro antibody, anti-La antibody, QuantiFERON-TB Gold, syphilis IgG antibody, and hepatitis B surface antigen and antibody. Positive results included hepatitis B antibody, hepatitis C antibody, and HIV-2 antibody. The patient denied overt symptoms suggestive of an immunocompromised status, including fever, chills, weight loss, or diarrhea. Initial treatment included mid-potency topical steroids with continued progression of the eruption. Following histopathologic and laboratory results indicating photolichenoid eruption, treatment with hydroxychloroquine 200 mg twice daily was resumed. The patient was counseled on the importance of sun protection and was referred to an infectious disease clinic for treatment of HIV. He was ultimately lost to follow-up before further laboratory workup was obtained. Therefore, his CD4+ T-cell count and viral load were not obtained.