Gender
Next, we evaluated variations based on gender (Table 2). Of 404 patients, 254 were female and 150 were male. Females preferred cream (127 vs 113.8 expected). Males exhibited preference for lotion (50 vs 42.3 expected) and ointment (46 vs 40.5 expected). Differences between genders were statistically significant (P=.023).
Ethnicity
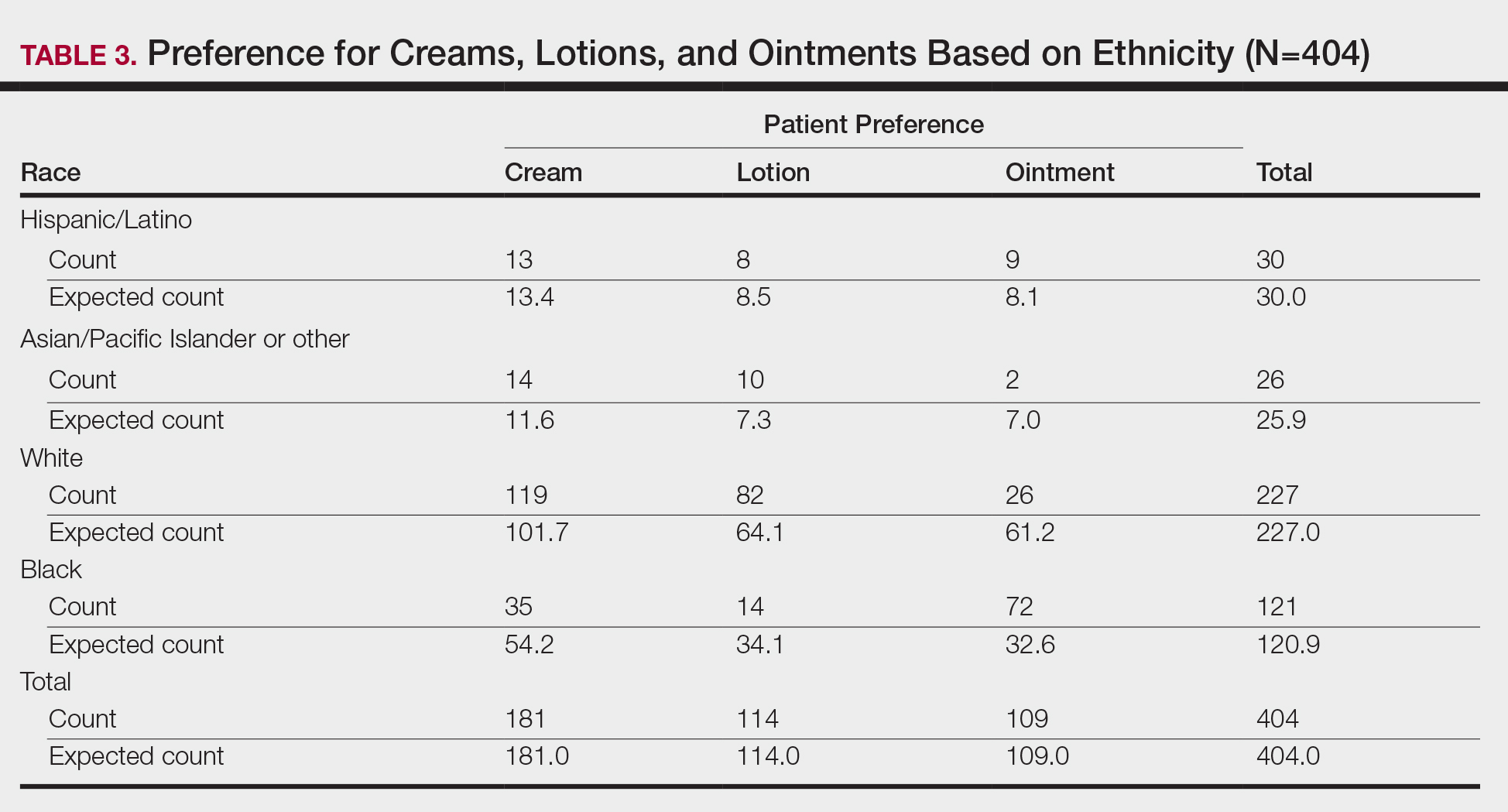
We then analyzed preferences based on ethnicity (Table 3). Of 404 patients, 30 were Hispanic/Latino, 26 were Asian/Pacific Islander or other, 227 were white, and 121 were black. Hispanic/Latino patients showed equivocal findings, aligning with expected counts. Asian/Pacific Islander or other patients exhibited slight preferences for cream (14 vs 11.6 expected) and lotion (10 vs 7.3 expected). White patients preferred cream (119 vs 101.7 expected) and lotion (82 vs 64.1 expected). Black patients showed strong preference for ointment (72 vs 32.6 expected). Differences in preferences based on ethnicity were statistically significant (P<.0001).
Comment
Topical medication is a mainstay of dermatologic therapy. Many topical preparations (or vehicles) exist, including ointments, creams, lotions, gels, solutions, and foams. Vehicle type not only influences bioavailability of the prepared medication but also has a notable impact on adherence and subsequent efficacy of the topical therapy.
Medication adherence is especially challenging in dermatology, as topical medications play a central role in treatment. Compliance with the medication regimen is paramount in treatment efficacy.1 In dermatology, adherence with oral medications is higher than it is for topical medications2; various factors contribute to this difference. Compliance may decline with topical treatment due to time-consuming application, misunderstanding about the disease or the treatment regimen, frequency of administration, dissatisfaction with efficacy or appearance, and other variables.3
Other factors have been found to be important to topical medication adherence; younger age, female gender, marriage, employment, nonsmoking, nondrinking, and higher cognitive ability were associated with higher topical medication adherence.4 Our study focused on one factor: identification of demographic-specific preferences that might have implications on adherence within the studied demographic groups.
It is known that individual preferences exist when patients are choosing a topical preparation. However, a PubMed search of articles indexed for MEDLINE using the terms topical, vehicle, preparation, adherence, and preference revealed few studies that examined the preference for topical vehicle by age, gender, or ethnicity.