In November 2019, the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) and the National Psoriasis Foundation (NPF) released their first set of recommendations for the management of pediatric psoriasis.1 The pediatric guidelines discuss methods of quantifying disease severity in children, triggers and comorbidities, and the efficacy and safety of various therapeutic agents. This review aims to discuss, in a condensed form, special considerations unique to the management of children with psoriasis as presented in the guidelines as well as grade A– and grade B–level treatment recommendations (Table).
Quantifying Psoriasis Severity in Children
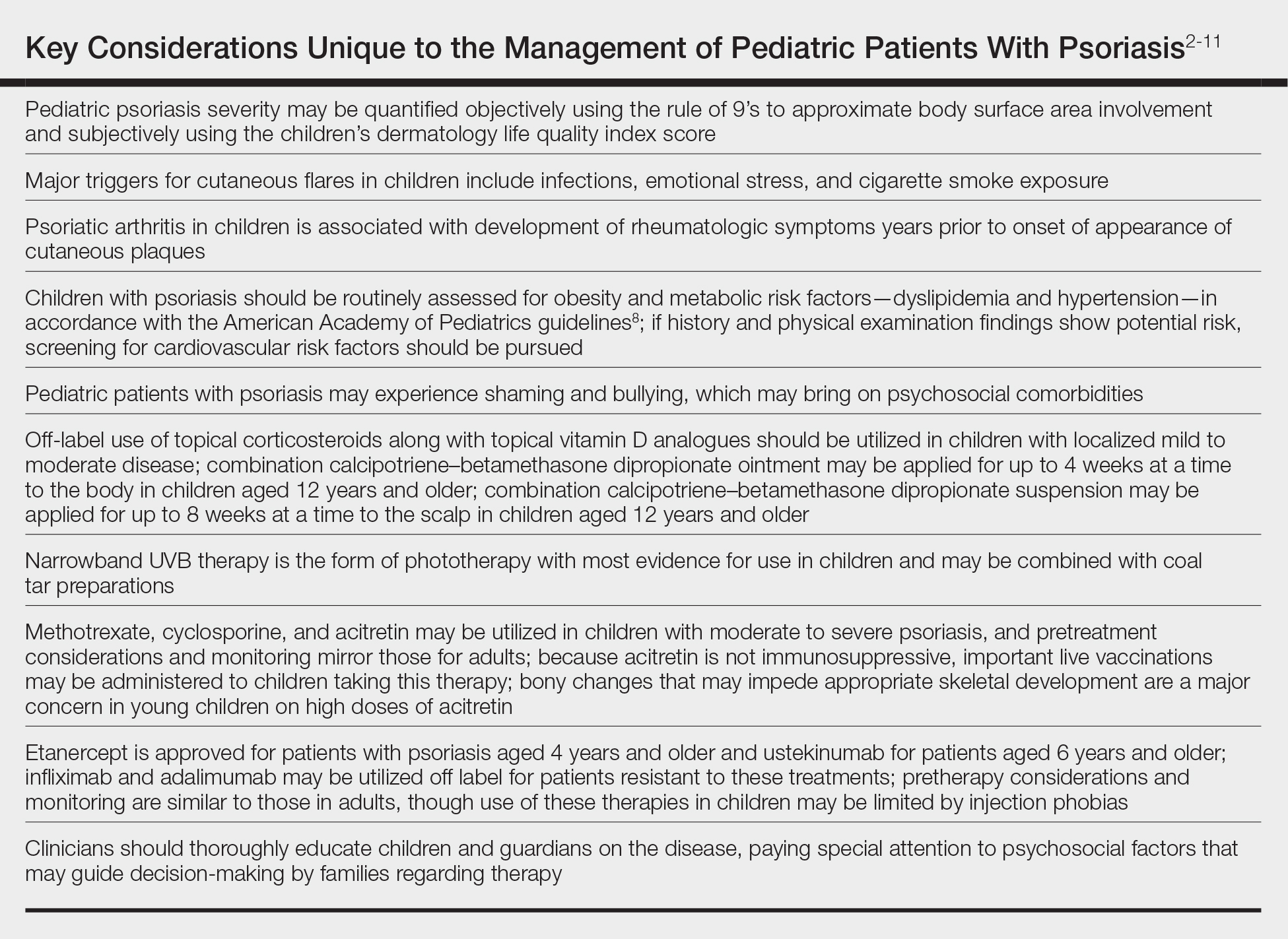
Percentage body surface area (BSA) involvement is the most common mode of grading psoriasis severity, with less than 3% BSA involvement being considered mild, 3% to 10% BSA moderate, and more than 10% severe disease. In children, the standard method of measuring BSA is the rule of 9’s: the head and each arm make up 9% of the total BSA, each leg and the front and back of the torso respectively each make up 18%, and the genitalia make up 1%. It also is important to consider impact on quality of life, which may be remarkable in spite of limited BSA involvement. The children’s dermatology life quality index score may be utilized in combination with affected BSA to determine the burden of psoriasis in context of impact on daily life. This metric is available in both written and cartoon form, and it consists of 10 questions that include variables such as severity of itch, impact on social life, and effects on sleep. Most notably, this tool incorporates pruritus,2 which generally is addressed inadequately in pediatric psoriasis.
Triggers and Comorbidities in Pediatric Patients
In children, it is important to identify and eliminate modifiable factors that may prompt psoriasis flares. Infections, particularly group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infections, are a major trigger in neonates and infants. Other exacerbating factors in children include emotional stress, secondhand cigarette smoke, Kawasaki disease, and withdrawal from systemic corticosteroids.
Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a burdensome comorbidity affecting children with psoriasis. The prevalence of joint disease is 15-times greater in children with psoriasis vs those without,3 and 80% of children with PsA develop rheumatologic symptoms, which typically include oligoarticular disease and dactylitis in infants and girls and enthesitis and axial joint involvement in boys and older children, years prior to the onset of cutaneous disease.4 Uveitis often occurs in children with psoriasis and PsA but not in those with isolated cutaneous disease.
Compared to unaffected children, pediatric patients with psoriasis have greater prevalence of metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors during childhood, including central obesity, hypertension, hypertriglyceridemia, hypercholesterolemia, insulin resistance, atherosclerosis, arrythmia, and valvular heart disease. Family history of obesity increases the risk for early-onset development of cutaneous lesions,5,6 and weight reduction may alleviate severity of psoriasis lesions.7 In the United States, many of the metabolic associations observed are particularly robust in Black and Hispanic children vs those of other races. Furthermore, the prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease is 3- to 4-times higher in children with psoriasis compared to those without.
As with other cutaneous diseases, it is important to be aware of social and mental health concerns in children with psoriasis. The majority of pediatric patients with psoriasis experience name-calling, shaming, or bullying, and many have concerns from skin shedding and malodor. Independent risk for depression after the onset of psoriasis is high. Affected older children and adolescents are at increased risk for alcohol and drug abuse as well as eating disorders.
Despite these identified comorbidities, there are no unique screening recommendations for arthritis, ophthalmologic disease, metabolic disease, cardiovascular disease, gastrointestinal tract disease, or mental health issues in children with psoriasis. Rather, these patients should be monitored according to the American Academy of Pediatrics or American Diabetes Association guidelines for all pediatric patients.8,9 Nonetheless, educating patients and guardians about these potential issues may be warranted.