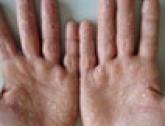
Psoriasis is a systemic disease that affects approximately 2% of the US population. Traditional treatment modalities include phototherapy, topical therapy, methotrexate, cyclosporine, and retinoids. Three tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitors have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of plaque psoriasis: etanercept, infliximab, and adalimumab. The combination of TNF inhibitors with phototherapy and topical and systemic agents may be effective in treating patients who are recalcitrant to monotherapy. We examine clinical trials that evaluated the efficacy and safety of combination treatments with TNF inhibitors. This review elucidates that combination therapy is both effective and well tolerated among patients with refractory psoriasis. Furthermore, combination therapy may allow for reduction of required treatment doses, thereby decreasing the potential for toxicity. It is important to note, however, that the studies reviewed here are limited in the long-term follow-up of patients. We conclude that dermatologists can safely and effectively incorporate combination therapy with TNF inhibitors in the treatment of patients with recalcitrant psoriasis.