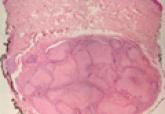
Myofibromatosis can be classified based on its clinical presentation as either solitary infantile myofibroma, congenital multiple myofibromatosis without visceral involvement, congenital generalized myofibromatosis with visceral involvement, or solitary adult myofibroma. Solitary adult myofibroma is a benign proliferation of myofibroblasts that most commonly presents as a firm superficial nodule on the skin or oral mucosa of young to middle-aged adults.