One of the most severe complications of systemic medications is the development of a life-threatening rash, especially toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN). Most patients can expect a full recovery if the complicating medication is discontinued early on in its course.1 When suspected TEN does not improve despite discontinuation of the detrimental medication, other diseases must be considered, particularly immunobullous and infectious etiologies. Treatment of these diseases differs substantially; therefore, a quick diagnosis is crucial. We present a case of a patient with an acute blistering eruption that was initially diagnosed and managed as TEN but physical examination and histopathologic confirmed another diagnosis. We review key examination findings that can help differentiate the causes of an acute blistering eruption with mucosal involvement, allowing for earlier diagnosis and treatment of these patients.
Case Report
An 85-year-old immunocompetent man was admitted to an outside hospital with a pruritic blistering eruption associated with myalgia, weakness, and fatigue of 3 weeks’ duration. The eruption initiated on the scalp and face and then spread down to the trunk and proximal arms and legs, with oral erosions also reported. An outside dermatologist was consulted on admission and performed a skin biopsy; the initial pathology was read as TEN. The patient was admitted to our institution on the same day, and all potentially complicating medications were stopped. He was treated with intravenous (IV) methylprednisolone sodium succinate 125 mg twice daily for 4 days and prednisone 40 mg daily for 9 days. With the rash worsening, the patient was restarted on methylprednisolone sodium succinate 40 mg every 8 hours approximately 3 weeks after admission, along with IV immunoglobulin at 2 g/kg over 3 days. When the patient did not respond to treatment, he was transferred to the University of California Irvine Medical Center for a higher level of care.
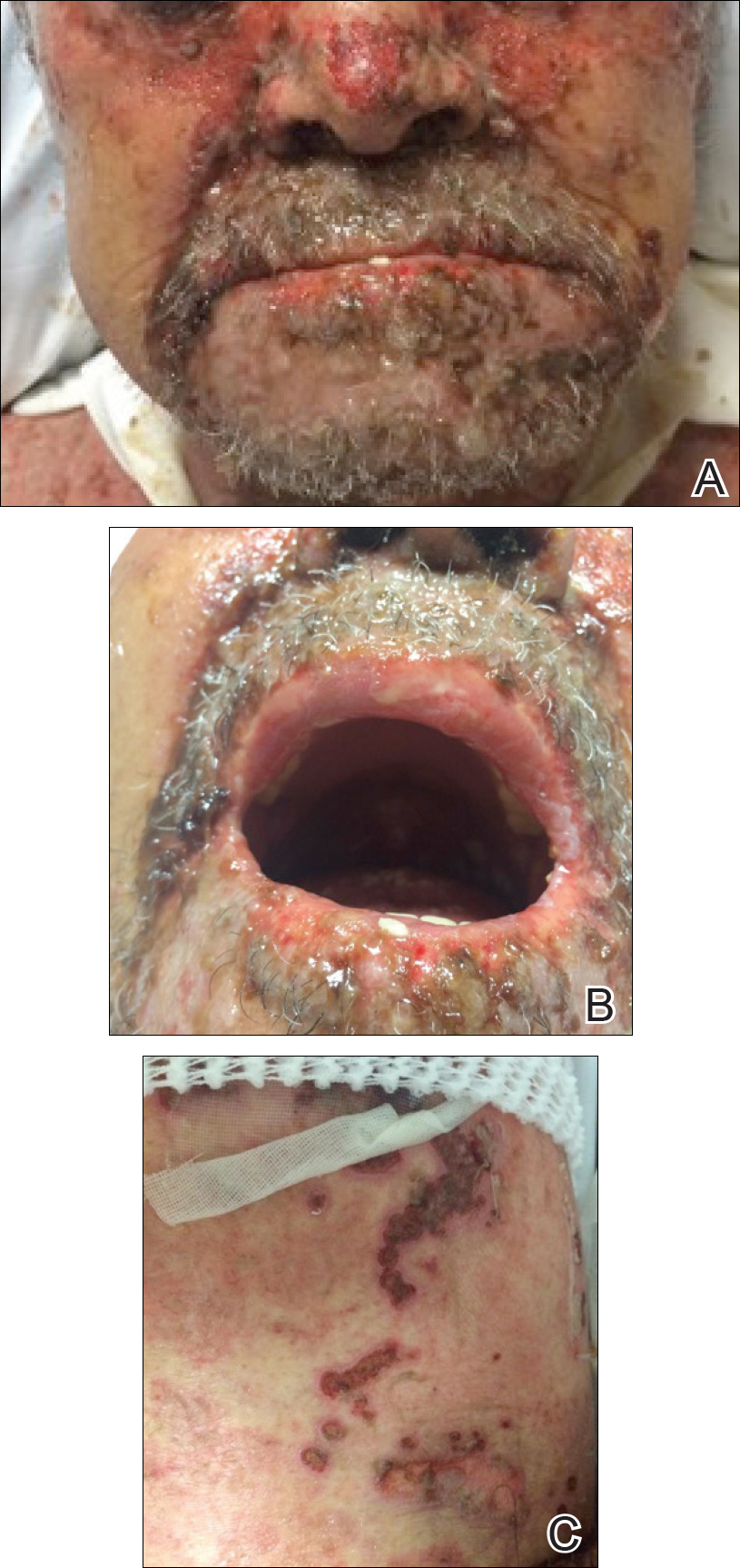
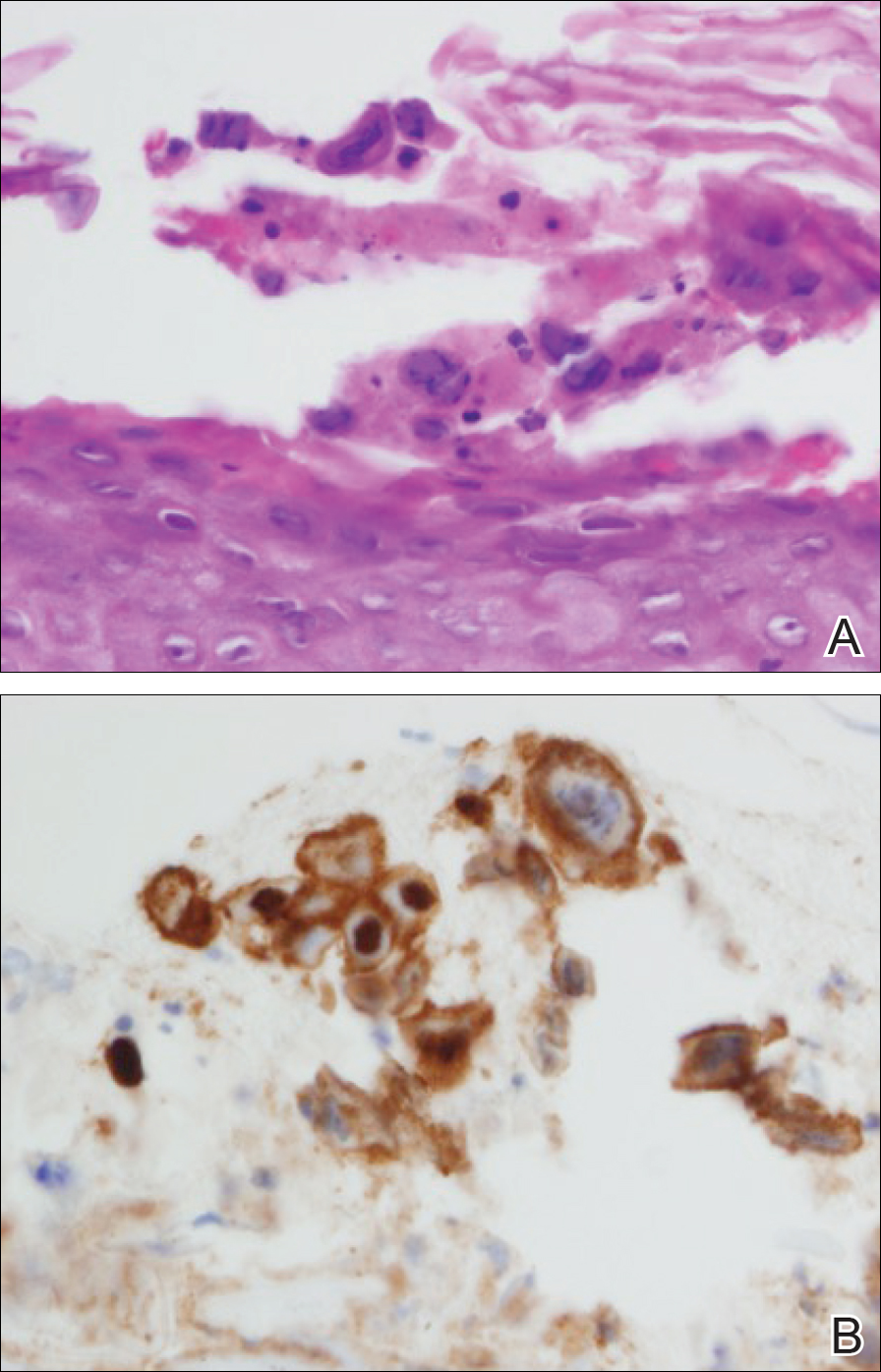
At that time, physical examination revealed numerous confluent erosions with honey-colored crust involving the entire face (Figure 1A) and sharp demarcation at the cutaneous lip (Figure 1B). There was a large erosion on the dorsal aspect of the tongue, but the rest of the oral mucosa was spared. The trunk and proximal extremities showed numerous grouped, punched-out erosions with scalloped borders (Figure 1C). A repeat skin biopsy showed an ulcer with viral cytopathic changes. Immunoperoxidase studies demonstrated positive staining for herpes simplex virus (HSV) type 1 (Figure 2). The original slides were a frozen section from an outside facility and could not be obtained. A tissue culture and direct fluorescent antibody also confirmed HSV-1, and the patient was diagnosed with disseminated herpes. He was rapidly tapered off of the steroids and started on IV acyclovir 10 mg/kg every 8 hours for 21 days. All prior erosions reepithelialized within 7 days of treatment (Figure 3). The patient had an otherwise uncomplicated hospital course and was discharged on hospital day 21.