People may be absorbing and ingesting potentially toxic chemicals from their cosmetic products, a new study suggests.
– per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Many of these chemicals were not included on the product labels, making it difficult for consumers to consciously avoid them.
“This study is very helpful for elucidating the PFAS content of different types of cosmetics in the U.S. and Canadian markets,” said Elsie Sunderland, PhD, an environmental scientist who was not involved with the study.
“Previously, all the data had been collected in Europe, and this study shows we are dealing with similar problems in the North American marketplace,” said Dr. Sunderland, a professor of environmental chemistry at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston.
PFAS are a class of chemicals used in a variety of consumer products, such as nonstick cookware, stain-resistant carpeting, and water-repellent clothing, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. They are added to cosmetics to make the products more durable and spreadable, researchers said in the study.
“[PFAS] are added to change the properties of surfaces, to make them nonstick or resistant to stay in water or oils,” said study coauthor Tom Bruton, PhD, senior scientist at the Green Science Policy Institute in Berkeley, Calif. “The concerning thing about cosmetics is that these are products that you’re applying to your skin and face every day, so there’s the skin absorption route that’s of concern, but also incidental ingestion of cosmetics is also a concern as well.”
The CDC says some of the potential health effects of PFAS exposure includes increased cholesterol levels, increased risk of kidney and testicular cancer, changes in liver enzymes, decreased vaccine response in children, and a higher risk of high blood pressure or preeclampsia in pregnant women.
“PFAS are a large class of chemicals. In humans, exposure to some of these chemicals has been associated with impaired immune function, certain cancers, increased risks of diabetes, obesity and endocrine disruption,” Dr. Sunderland said. “They appear to be harmful to every major organ system in the human body.”
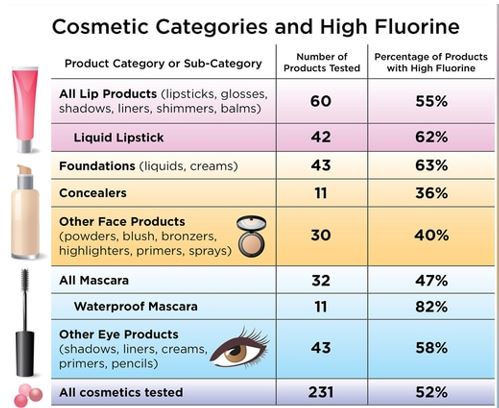
For the current study, published online in Environmental Science & Technology Letters, Dr. Bruton and colleagues purchased 231 cosmetic products in the United States and Canada from retailers such as Ulta Beauty, Sephora, Target, and Bed Bath & Beyond. They then screened them for fluorine.Three-quarters of waterproof mascara samples contained high fluorine concentrations, as did nearly two-thirds of foundations and liquid lipsticks, and more than half of the eye and lip products tested.
The authors found that different categories of makeup tended to have higher or lower fluorine concentrations. “High fluorine levels were found in products commonly advertised as ‘wear-resistant’ to water and oils or ‘long-lasting,’ including foundations, liquid lipsticks, and waterproof mascaras,” Dr. Bruton and colleagues wrote.
When they further analyzed a subset of 29 products to determine what types of chemicals were present, they found that each cosmetic product contained at least 4 PFAS, with one product containing 13.The PFAS substances found included some that break down into other chemicals that are known to be highly toxic and environmentally harmful.
“It’s concerning that some of the products we tested appear to be intentionally using PFAS, but not listing those ingredients on the label,” Dr. Bruton said. “I do think that it is helpful for consumers to read labels, but beyond that, there’s not a lot of ways that consumers themselves can solve this problem. ... We think that the industry needs to be more proactive about moving away from this group of chemicals.”
Dr. Sunderland said a resource people can use when trying to avoid PFAS is the Environmental Working Group, a nonprofit organization that maintains an extensive database of cosmetics and personal care products.
“At this point, there is very little regulatory activity related to PFAS in cosmetics,” Dr. Sunderland said. “The best thing to happen now would be for consumers to indicate that they prefer products without PFAS and to demand better transparency in product ingredient lists.”
A similar study done in 2018 by the Danish Environmental Protection Agency found high levels of PFAS in nearly one-third of the cosmetics products it tested.
People can also be exposed to PFAS by eating or drinking contaminated food or water and through food packaging. Dr. Sunderland said some wild foods like seafood are known to accumulate these compounds in the environment.
“There are examples of contaminated biosolids leading to accumulation of PFAS in vegetables and milk,” Dr. Sunderland explained. “Food packaging is another concern because it can also result in PFAS accumulation in the foods we eat.”
Although it’s difficult to avoid PFAS altogether, the CDC suggests lowering exposure rates by avoiding contaminated water and food. If you’re not sure if your water is contaminated, you should ask your local or state health and environmental quality departments for fish or water advisories in your area.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.