Case 1 Multiparous woman presents with heavy regular menses
Over the past several years, a 34-year-old woman has noted increasing intensity and duration of menstrual flow, which now persists for 8 days and includes clots “the size of quarters” and soaks a pad within 1 hour. Sometimes she misses or leaves work on her heaviest days of flow. She reports that menstrual cramps prior to and during flow are increasingly bothersome and do not respond adequately to ibuprofen. She intermittently uses condoms for contraception. She does not wish to be pregnant currently; however, she recently entered into a new relationship and may wish to conceive in the future.
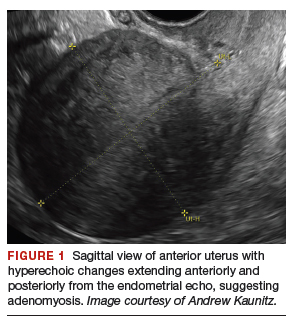
On bimanual examination, the uterus appears bulky. Her hemoglobin is 10.9 g/dL with low mean corpuscular volume and a serum ferritin level indicating iron depletion. Pelvic ultrasonography suggests uterine adenomyosis; no fibroids are imaged (FIGURE 1).
You advise the patient to take ferrous sulfate 325 mg every other day. After discussion with the patient regarding different treatment options, she chooses to proceed with placement of a 52-mg levonorgestrel (LNG) intrauterine device (IUD; Mirena or Liletta).
Case 2 Older adolescent presents with irregular bleeding
A 19-year-old patient reports approximately 6 bleeding episodes each year. She reports the duration of her bleeding as variable, and sometimes the bleeding is heavy with small clots passed. She has been previously diagnosed with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Combination estrogen-progestin oral contraceptives have been prescribed several times in the past, but she always has discontinued them due to nausea. The patient is in a same-sex relationship and does not anticipate being sexually active with a male. She reports having to shave her mustache and chin twice weekly for the past 1 to 2 years.
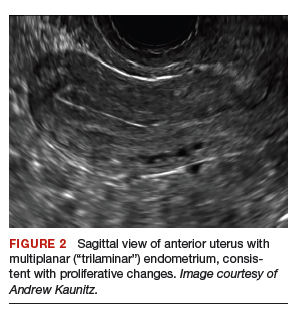
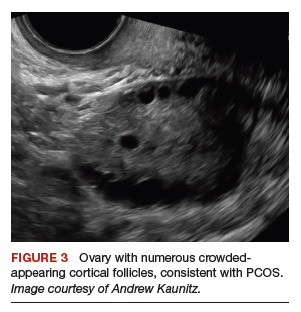
On physical examination, the patient is obese (body mass index [BMI], 32 kg/m2), facial acne and hirsutism are present, and hair extends from the mons toward the umbilicus. Bimanual examination reveals a normal size, mobile, nontender uterus without obvious adnexal pathology. Pelvic ultrasonography demonstrates a normal-appearing uterus with multiplanar endometrium (consistent with proliferative changes) (FIGURE 2). Ovarian imaging demonstrates ≥12 follicles per image (FIGURE 3).
After reviewing various treatment options, you prescribe oral medroxyprogesterone acetate 20 mg (two 10-mg tablets) daily in a continuous fashion. You counsel her that she should not be surprised or concerned if frequent or even continuous bleeding occurs initially, and that she should continue this medication despite the occurrence of such.
About one-third of all women experience abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) sometime during their lifetime and AUB can impair quality of life.1 Surgical management, including hysterectomy and endometrial ablation, plays an important role in the management of AUB in patients who do not desire future pregnancies. However, many cases of AUB occur in women who may not have completed childbearing or in women who prefer to avoid surgery.2 AUB can be managed effectively medically in most cases.1 Accordingly, in this review, we focus on nonsurgical management of AUB.
Continue to: Because previously used terms, including...