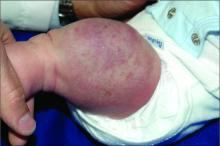
The history of a brownish to pink patch with color change and rapid growth within the first year combined with the exam findings, are suggestive of a tufted angioma, though the findings presented may be nonspecific.
A tufted angioma is a rare vascular tumor of infancy or early childhood, that is present at birth in approximately half of cases. It may initially present as a faint pink to brown plaque, but develops as a firm, red to violaceous nodule or plaque, usually with “lumpiness” or nodularity.1-3 Lesions usually are infiltrative with indistinct borders. They are named for their histologic appearance, with lobules of capillaries which appear as “tufts” in the dermis and subdermis with “cannonball” appearance, and are considered to be on a spectrum with another vascular tumor called kaposiform hemangioendothelioma (KHE).4 These vascular tumors can trigger Kasabach-Merritt syndrome, a disease process in which vascular tumors trap platelets and clotting factors, resulting in a life-threatening thrombocytopenia and consumptive coagulopathy with a high risk of bleeding and high-output heart failure.5
What’s the differential diagnosis?
The differential diagnosis of tufted angioma includes other potentially large vascular lesions including infantile hemangioma, congenital hemangioma, port-wine birth marks (capillary malformations), hemangioendotheliomas, and rhabdomyosarcomas.
Infantile hemangiomas (IH) are common vascular tumors of infancy seen in 4%-5% of infants that are characterized by a growth and involution phase. Classically, lesions can be absent or minimally evident at birth, becoming noticeable within the first months of life with a rapid growth phase and typical progression to bright red papules, nodules, or plaques. Deeper hemangiomas may appear more skin colored on the surface with a bluish coloration underneath. They are usually more discreet, with relatively defined borders. Diagnosis is typically clinical and many IHs self-resolve, albeit with residual findings including skin atrophy, scarring, and telangiectasia. Observation or topical timolol are first-line treatment options for more superficial lesions while systemic propranolol is the treatment of choice for deeper IHs or those resulting in possible airway or vision compromise.
Congenital hemangiomas (CH) are another type of vascular growth characterized by a solitary erythematous to violaceous plaque or nodule present at birth with overlying telangiectasia. CHs can be subdivided into categories including rapidly involuting (RICH), partially involuting (PICH), and noninvoluting (NICH). Diagnosis is usually clinical and, depending on the subtype, treatment can involve watchful waiting (for RICHs) or more active intervention such as pulse dye laser or surgical resection (for PICHs or NICHs). The growing nature of this patient’s mass makes a diagnosis of CH unlikely.
Port-wine birth mark, also known as nevus flammeus, is a vascular malformation that appears at birth as a nonpalpable irregular erythematous to violaceous macular plaque. Port-wine stains may be isolated birthmarks, or associated with Sturge-Weber syndrome, complex vascular malformations, or soft-tissue overgrowth. Klippel-Trenauny syndrome (KTS) describes capillary-venous malformations with limb overgrowth, with or without lymphatic malformations, and many are associated with somatic mutations in the PIK3CA gene. While KTS could be considered in this patient, the nodular appearance with lumpy texture and rapid growth makes a vascular tumor more likely.
Rhabdomyosarcoma is a malignancy of skeletal muscle lineage and the most common soft tissue tumor in pediatrics. Cutaneous rhabdomyosarcomas present as erythematous nodules, markedly firm, often “fixed” to deep tissue. A rapidly growing atypical, firm tumor of infancy should raise the consideration of rhabdomyosarcoma and imaging and biopsy are appropriate for evaluation.