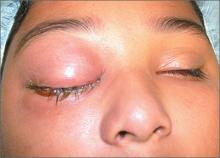
This patient had a severe case of periorbital cellulitis. The ENT doctor ordered a computed tomography scan of the sinuses, which showed ethmoid and maxillary sinusitis on the right side with some proptosis. Periorbital cellulitis is often seen in conjunction with sinusitis in children and adults.
Mild cases with minimal upper eyelid swelling can be treated with oral antibiotics, whereas moderate to severe cases may require hospitalization for IV antibiotics and evaluation for surgical intervention. Possible complications of untreated periorbital cellulitis include orbital cellulitis, blindness, cavernous sinus thrombosis, and death.
This patient was prepped for sinus surgery to drain the infected sinuses. She also received IV antibiotics. Fortunately, she responded well to treatment and went home without any complications.
Photo courtesy of Frank Miller, MD. Text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Usatine R. Cellulitis. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:693-697.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com