Frequently misdiagnosed, streptococcal intertrigo more commonly affects infants and toddlers but is rarely reported, especially compared with other Streptococcus pyogenes infections, including impetigo, erysipelas, and cellulitis.1
Intertrigo, meaning “between” (inter) and “to rub” (terere) in Latin, describes any skin disorder involving two opposing skin surfaces that touch or rub to cause friction.2 The continuous chaffing, coupled with moisture trapped within the skin folds, leads to irritation and maceration, which provides an ideal environment for pathogens to thrive. Thus, frictional dermatitides that arise may become secondarily infected with one or more microorganisms, such as Candida albicans, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes, and even organisms less commonly associated with cutaneous infection, such as Proteus mirabilis.3
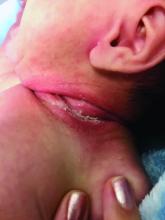
Intertrigo caused by Streptococcus pyogenes is classically characterized by fiery erythema and moist maceration. Homogeneous in appearance, lesions are discretely demarcated and notably lack satellite lesions, unlike in candidal intertrigo. Distinctly foul odor and worsening or persistence of rash despite antifungal treatment also are helpful features in distinguishing streptococcal intertrigo from candidal intertrigo.4 These characteristics are essential to consider because streptococcal intertrigo is most commonly initially misdiagnosed as candidal intertrigo, which is the most common type of intertrigo.5Streptococcal intertrigo may affect any intertriginous area, but most commonly it affects the folds of the neck; this is likely because of the combination of the deep folds that develop in shorter, infantile necks and the moisture from drool and saliva that pools in the area.5,6 In addition to these cervical folds, other intertriginous areas commonly are affected, including the inguinal, axillary, popliteal, posterior auricular, perianal, and genital folds.
Perianal streptococcal disease may present in a similar manner as streptococcal intertrigo, manifesting as well-demarcated, beefy red plaques in the skin folds around the anus and, in females, frequently perivaginally.7 Unlike streptococcal intertrigo, perianal streptococcal disease is often characterized by pain, pruritus, and fissuring of the involved area.8 It is associated with pharyngeal colonization of group A beta-hemolytic streptococci.7
Patients may be well appearing, or they may present with irritability and low-grade fever; only one case in the literature has described development of bacteremia secondary to cervical streptococcal intertrigo that had developed in a 12-month-old infant.1Diagnosis is straight forward and may be confirmed by a positive streptococcal rapid antigen test of swab specimens of one or more surfaces of affected skin or by culture from a skin swab yielding growth of the organism.1,5 Skin biopsy is not necessary. If the index of suspicion for candida is high, a potassium hydroxide preparation and culture may be performed. Checking serum anti-DNase B antibodies, antistreptolysin O, and pharyngeal cultures is often unrevealing.9 A urinalysis may be performed to assess for poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis if the patient later develops facial or orbital edema, hypertension, hematuria, or lethargy.9
Treatment consists of systemic antistreptococcal therapy; oral amoxicillin and penicillin frequently have been used.9 Moisture in the area should be reduced with application of absorptive powders and physical barriers, such as zinc oxide, after gentle cleansing of the area.5
Of note, in patients with underlying atopic dermatitis, secondary infection with Streptococcus pyogenes may exacerbate atopic dermatitis, resulting in a flare of inflammation that persists even after appropriate therapy of the Streptococcus pyogenes. In these patients, it is reasonable and beneficial to treat with concomitant topical corticosteroids.9Streptococcus pyogenes infection also has been identified as a trigger for guttate psoriasis. Thus, if coin-shaped, erythematous lesions with scale are appreciated, a diagnosis of guttate psoriasis should be considered and the presence of a preceding streptococcal infection inquired about.5 Although islands of erythema and scale may resemble satellite lesions, it is important to include guttate psoriasis in the differential and not confound these entities because they lead to favoring of differing diagnoses and treatment options.4Other diagnoses to consider when evaluating dermatitides affecting skin folds include: other infectious causes, which may be ruled out by fungal or bacterial culture; inverse psoriasis, which will frequently demonstrate scale; atopic dermatitis, which will be pruritic with history of atopy; irritant or contact dermatitis, which will often have correlating clinical history; seborrheic dermatitis, which will often involve greasiness and scale; and less commonly, acrodermatitis enteropathica, which will be accompanied by diarrhea and hair loss.2,9 Scabies also may be on the differential if the patient endorses severe pruritus with close contacts with similar symptoms.
Ms. Han is a medical student at the University of California, San Diego. Dr. Eichenfield is chief of pediatric and adolescent dermatology at Rady Children’s Hospital–San Diego. He is vice chair of the department of dermatology and a professor of dermatology and pediatrics at the university. They had no conflicts of interest or disclosures to report.
References
1. Pediatr Dermatol. 2014 Mar-Apr;31(2):e71-2.
2. Clin Dermatol. 2011 Mar-Apr;29(2):173-9.
3. Pediatrics. 2003 Dec;112(6 pt 1):1427-9.
4. BMJ Case Rep. 2018 Mar 20. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2018-224179.
5. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2012 Aug;31(8):872-3.
6. J Pediatr. 2015 May;166(5):1318.
7. J Pediatr. 2015 Sep;167(3):687-93.e1-2.