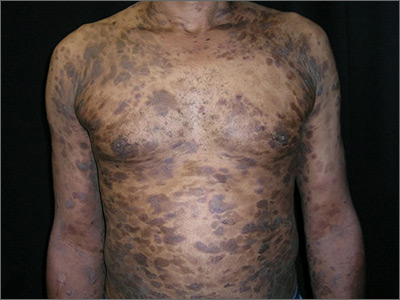
The differential diagnosis included psoriasis, drug eruption, and a cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A drug eruption could have been due to an over-the-counter medication or supplement, so the lack of improvement from stopping the antihypertensive medication did not rule out this diagnosis. Psoriasis does not always show erythema in persons of color, but these plaques were not typical of psoriasis. (There also were some flat patches that were even less typical of psoriasis.)
The FP performed a 4-mm punch biopsy on one of the hyperpigmented plaques on the abdomen. A 4-mm punch biopsy is generally an ideal method for determining the cause of an unknown skin rash, and it is usually better to choose a lesion on the upper body rather than below the waist if the rash is widespread. (See the Watch & Learn video on “Punch biopsy.”)
The FP also prescribed a 1-pound tub of 0.1% triamcinolone ointment for symptomatic relief as this could help any of the possible diagnoses being considered. The pathology report came back as mycosis fungoides, the most common type of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
The patient was sent to Hematology/Oncology for further evaluation and treatment. Mycosis fungoides can have both patches and plaques and frequently involves the trunk more than the extremities (which was the situation in this case). It is important to consider uncommon diagnoses like this in the differential when the initial diagnosis does not appear to be responding to treatment or there is something atypical about the presentation of an expected diagnosis.
Photos and text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. This case was adapted from: Chacon G, Nayar A, Usatine R, Smith M. Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al. Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine. 3rd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2019:1124-1131.
To learn more about the newest 3rd edition of the Color Atlas and Synopsis of Family Medicine, see: https://www.amazon.com/Color-Atlas-Synopsis-Family-Medicine/dp/1259862046/
You can get the Color Atlas of Family Medicine app by clicking on this link: usatinemedia.com