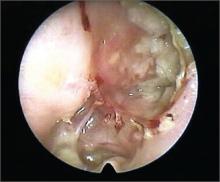
The patient had a cholesteatoma.
A cholesteatoma is similar to an epidermal inclusion cyst in the skin and causes the production of keratinaceous material that fills the middle ear, causing hearing loss and otorrhea. Oral and/or topical antibiotics are not effective at treating a cholesteatoma. The cholesteatoma often destroys the ossicles, which contributes to conductive hearing loss. A computed tomography scan can determine the extent of involvement and help the physician plan for surgery. Surgery is the definitive treatment to remove all of the abnormal tissue and prevent recurrence.
Text for Photo Rounds Friday courtesy of Richard P. Usatine, MD. Photo courtesy of Vladimir Zlinsky, MD, in Roy F. Sullivan, PhD. Audiology Forum: video otoscopy, www.rcsullivan.com.
This case was adapted from: Rayala B. Otitis media: acute otitis and otitis media with effusion. In: Usatine R, Smith M, Mayeaux EJ, et al, eds. Color Atlas of Family Medicine. 2nd ed. New York, NY: McGraw-Hill; 2013:170-179.
To learn more about the Color Atlas of Family Medicine, see: http://www.amazon.com/Color-Family-Medicine-Richard-Usatine/dp/0071769641/ref=dp_ob_title_bk
You can now get the second edition of the Color Atlas of Family Medicine as an app for mobile devices by clicking this link: http://usatinemedia.com/