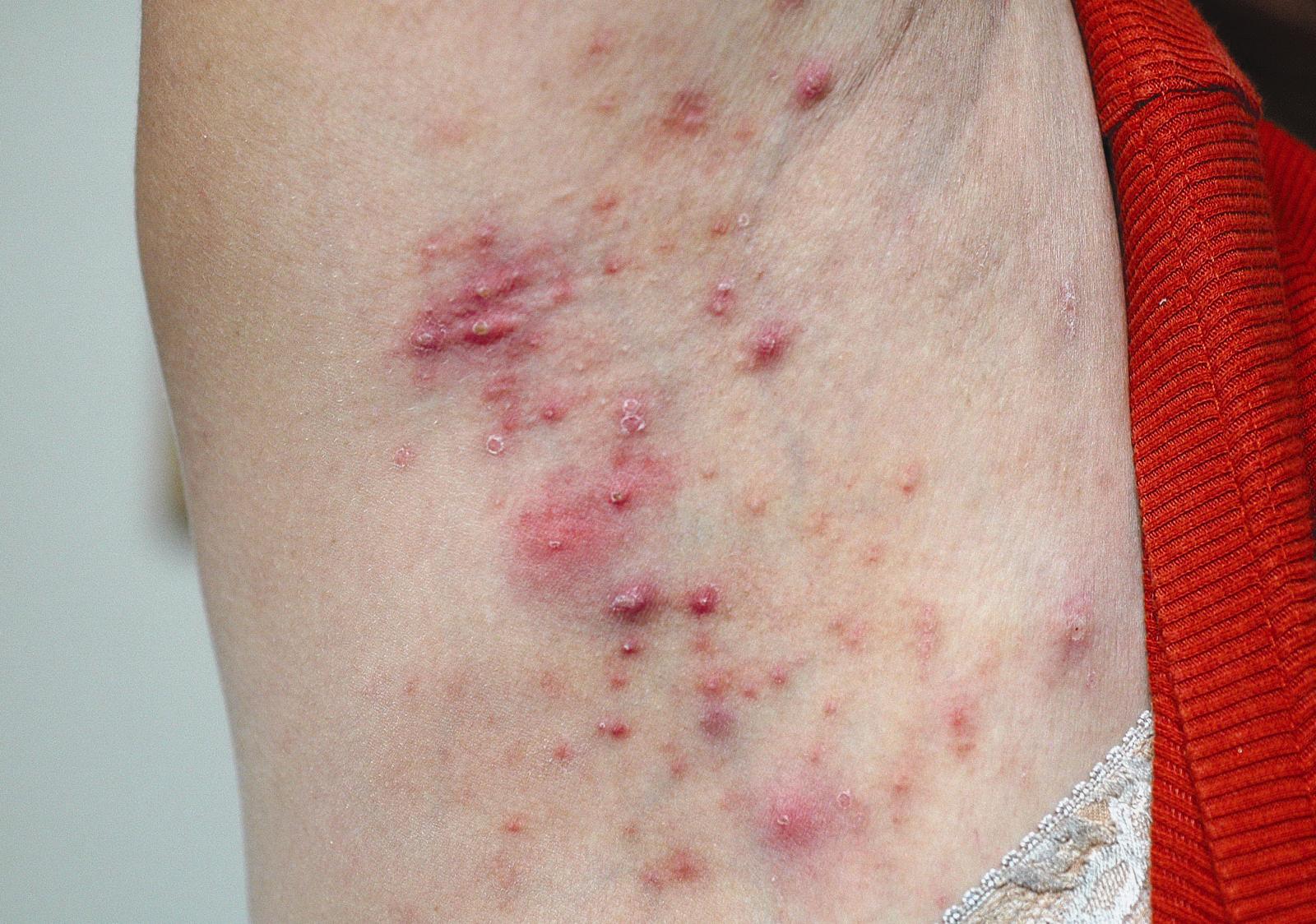
The acute nature of the process led the physician to favor a diagnosis of bacterial folliculitis; the culture came back positive for methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) sensitive to doxycycline.
Community-acquired MRSA outbreaks have been associated with participation in team sports, living in prison, dormitory or group home settings, IV drug use, sharing personal items, and men who have sex with men. However, the prevalence of MRSA infections in patients without any recognized risk factors, like this patient, is increasing.
Initial empiric treatment for the patient included doxycycline 100 mg daily and topical treatment with clindamycin 1% lotion twice a day. Once the culture came back, the physician instructed the patient to continue the initial medications and apply mupirocin 2% ointment to the nares twice a day for 1 week to eliminate the possibility of a staphylococcal carrier state.
At follow-up 2 weeks later, only a few excoriated papules and some post-inflammatory erythema remained. The topical clindamycin lotion and the doxycycline were continued for an additional 30 days, at which time the patient was clear and treatment was discontinued.
Adapted from:
Plotner AN, Brodell RT. Photo rounds: bilateral axillary pustules. J Fam Pract. 2008;57:253-255.